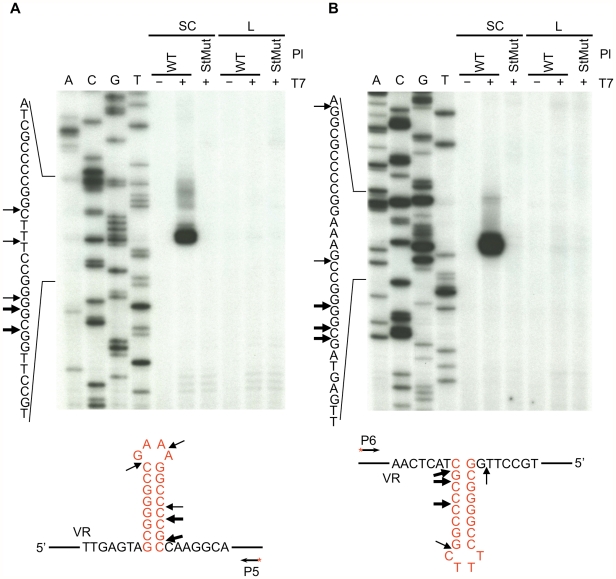
Figure 3. Hairpin/cruciform structure formation in negatively supercoiled DNA.
Primer extension assays were used to identify T7 endonuclease I cleavage sites in plasmid DNA containing either the WT or StMut target sequences. (A) Top strand cleavage, (B) bottom strand cleavage. Supercoiled or linearized plasmid DNA was either left untreated (−) or digested with T7 endonuclease I (+) followed by primer extension. Sequence ladders are shown to the left and primer extension termination sites in supercoiled WT plasmid DNA are shown underneath the gels. Thick and thin arrows designate major and minor cleavage sites, respectively. The exact positions of cleavage sites are +/−2–3 nt due to uncertainty resulting from compression of the sequence ladder in the hairpin/cruciform region caused by DNA secondary structure. The heavily labeled major products on both strands represent multiple adjacent cleavage sites which were resolved at lower exposures. The figure is representive of results obtained from multiple independent experiments. P5 and P6 (Table 1) are the 5′ end-labeled primers used for primer extensions in A and B, respectively. SC, supercoiled plasmids; L, linearized plasmids; Pl, plasmid; T7, T7 endonuclease I.