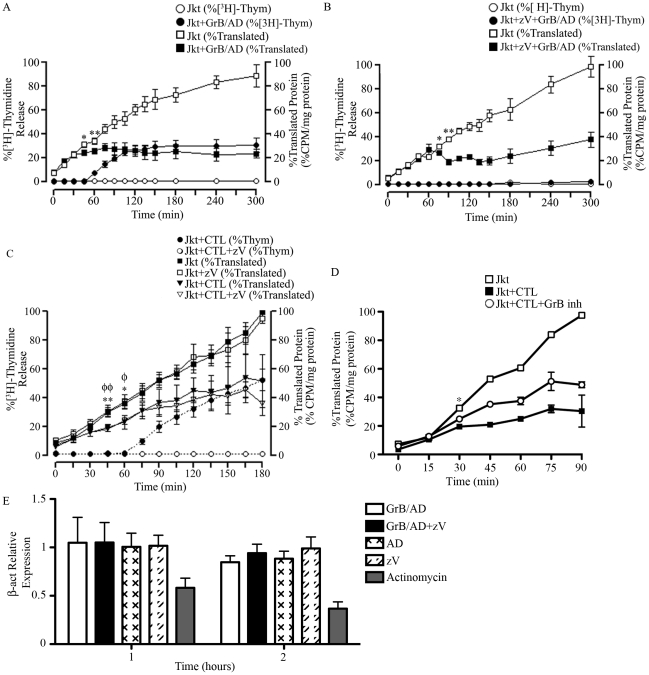
Figure 5. GrB or CTL treatment decrease translational rate in Jurkat cells independently of caspase-mediated DNA fragmentation.
(A and B) Jurkat cells were treated with GrB (1 µg/ml) for 300 min. At 15 min interval, cells were assessed for DNA fragmentation (%[3H]-Thymidine Release) and translational rate (% Translated Protein). (B) The pan-caspase inhibitor zVAD-fmk (zV) was used to evaluate the role of caspases. (For (A) and (B); n = 4 of 4 independent experiments). (C) Jurkat cells were treated with CTL for 180 min. As in (A) and (B), DNA fragmentation and translational rate was assessed at 15 min intervals. Statistical significance: p<0.05 (* and φ) p<0.01 (** and φφ); n = 3, where * compares statistical significance of % translated protein of Jurkat cells+zVAD-fmk (Jkt+zV) vs. Jurkat cells+zV+CTL; and φ compares Jkt vs. Jkt+CTL; (n = 3 of 3 independent experiments). (D) Jurkat cells were treated with CTL for 90 min in the presence of the GrB inhibitor L-038587-00Y001 (GrB inh). %Translated protein was assessed at 15 min intervals. Statistical significance: p<0.05 (* and φ), where * compares statistical significance of % translated protein of Jurkat cells+CTL vs. Jurkat cells+CTL+L−038587−00Y001; (n = 3 of 3 independent experiments). (E) qPCR analysis of β-actin (β-act) relative expression at 1 and 2 hr post GrB/AD treatment; (n = 3 of 3 independent experiments).