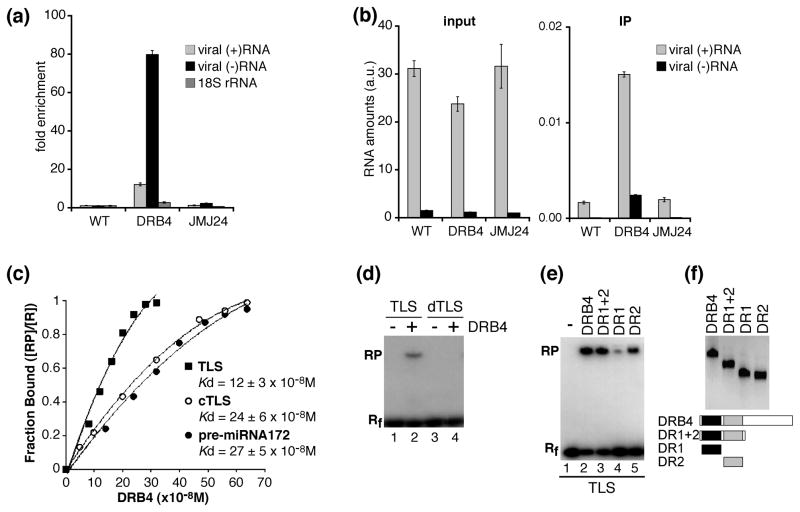
Figure 6. DRB4 interacts with viral RNA.
(a, b) DRB4 is associated with viral (+)RNA and (−)RNA in vivo.
Immunoprecipitations were performed using FLAG-specific antibodies and extracts from leaves of TYMV-infected WT plants (WT), 35S:DRB4-FLAG plants (DRB4) and 35S:FLAG-JMJ24 plants (JMJ24). Total RNA was extracted from an aliquot of each extract. The RNA amounts in total RNA (input) and immunoprecipitates (IP) were assessed by strand-specific RT-qPCR using for each target a serially diluted cDNA fragment to generate standard curves. The RNA amounts were normalized by luciferase transcript levels, which had been added to each sample before RNA purification in order to monitor the efficiency of RNA recovery.
(a) The fold enrichment of viral (+)RNA and (−)RNA and 18S rRNA was calculated by dividing luciferase-normalised RNA amount in the immunoprecipitates by luciferase normalized RNA amount in the input and setting the value obtained for WT plants to 1.
(b) The luciferase-normalized viral RNA amounts are presented in arbitrary units (a.u.) corresponding to viral RNA amounts divided by the luciferase amounts.
Error bars represent standard deviations from results of three technical replicates. The control reactions without reverse transcriptase prepared and analyzed in parallel were negative.
A higher enrichment of viral (−)RNA with respect to (+)RNA and a higher enrichment for both viral RNAs with respect to 18S rRNA in immunoprecipitates obtained from DRB4-FLAG plants was observed in at least 2 immunoprecipitation experiments.
(c–f) DRB4 interacts with structured RNAs in vitro.
(c) Determination of apparent dissociation constant (Kd) for DRB4 binding to TYMV TLS, TLS complementary RNA (cTLS) and pre-miRNA172 by gel mobility shift assays. Labeled RNA probes were incubated with increasing concentrations of full-length DRB4 protein (0–320nM for TLS and 0–640nM for cTLS and pre-miRNA172). The presented results are the average of 3 experiments for each substrate.
(d) Gel shift mobility assays were performed full-length DRB4 protein (lanes 2, 4) and with labeled TLS (lane 2) or denatured TLS (dTLS) which had been heat-treated prior to the assay (lane 4). The migration of free RNA probes is shown in lanes 1 and 3.
(e) Gel shift mobility assays were performed with labeled TYMV TLS and full-length DRB4 protein (lane 2) or its deletion derivatives containing DR1 (lane 4) and DR2 (lane 5) or both motifs (lane 3). The migration of free RNA probe is shown in lane 1.
(f) Western blot analysis (upper panel) and schematic representation (lower panel) of recombinant proteins used for gel mobility shift assays shown in (e). DR1: dsRNA binding motif 1 (black boxes), DR2: dsRNA binding motif 2 (grey boxes).
Rf: free RNA, RP: protein-bound RNA, R = Rf+RP