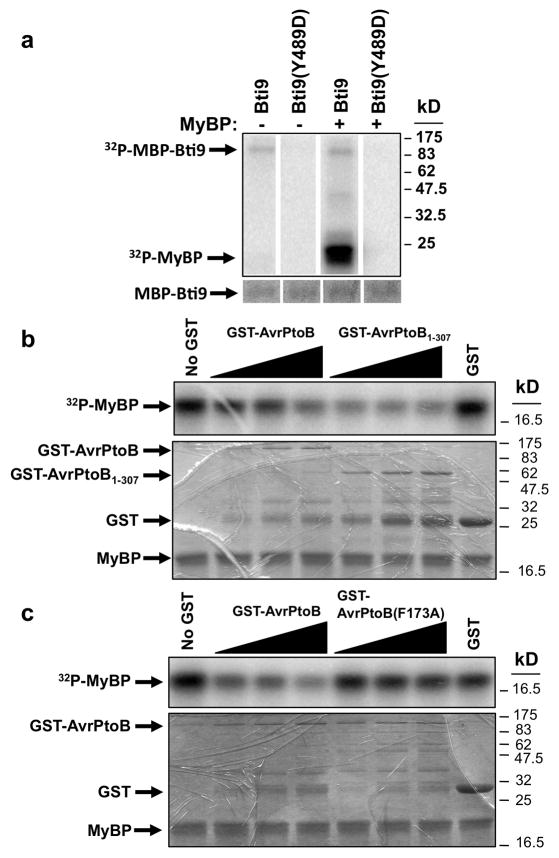
Figure 5. Bti9 is an active kinase whose activity is inhibited by AvrPtoB in vitro.
The top panel in each part shows a phosphor-image of the kinase assay. The bottom panel in parts B and C shows the Coomassie-stained gel that was used for phosphor-imaging of the kinase assay. (A) Bti9 encodes an active kinase. A maltose-binding protein (MBP) fusion to Bti9 weakly autophosphorylated and strongly trans-phosphorylated myelin basic protein (MyBP). Substitution of Y to D at amino acid 489 abolished Bti9 kinase activity. Reactions without MyBP were used as controls. The Coomassie-stained gel shows equal abundance of Bti9 or Bti9(Y489D) protein (barely visible because only 200 ng was used per lane). (B) AvrPtoB and AvrPtoB1-307 inhibited Bti9 kinase activity. Addition of GST-AvrPtoB or GST-AvrPtoB1-307 fusion proteins to the Bti9 kinase assays reduced the ability of Bti9 to phosphorylate MyBP in a dose-dependent manner. Top panel: first lane shows phosphorylation of MyBP by Bti9 without addition of AvrPtoB or AvrPtoB1-307. The next six lanes show the assay with addition of 2.5, 5.0, or 7.5 μg of GST-AvrPtoB or GST-AvrPtoB1-307, respectively. The last lane shows addition of GST alone did not inhibit Bti9 kinase activity. (C) The F173A substitution abolished the ability of AvrPtoB to inhibit Bti9 kinase activity. Top panel: first lane shows phosphorylation of MyBP by Bti9 without addition of AvrPtoB. The next six lanes show the assay with addition of 2.5, 5.0, or 7.5 μg of GST-AvrPtoB or GST-AvrPtoB(F173A), respectively. The last lane shows addition of GST alone did not inhibit Bti9 kinase activity.