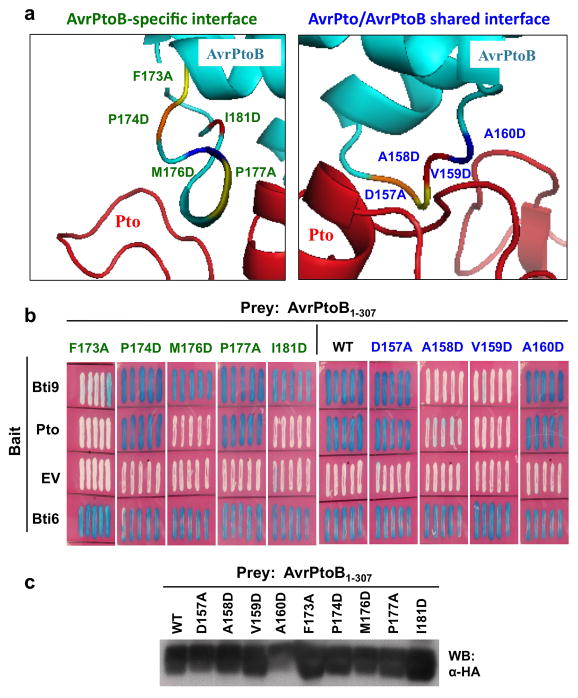
Figure 6. Bti9 and Pto interact with AvrPtoB1-307 in a similar but not identical way.
(A) Close-up of the crystal structure of the complex between AvrPtoB (in turquoise) and Pto (in red) (Dong, et al. 2009). The interface with Pto that is specific to AvrPtoB is shown in the left panel and the interface shared by both AvrPtoB and AvrPto is shown in the right panel. Residues at which amino acid substitutions were made are shown and their positions indicated in different colors (Dong, et al. 2009). (B) Interactions in a yeast two-hybrid assay of Bti9 or Pto with AvrPtoB1-307 and variants. Blue patches indicate a positive interaction. A non-specific AvrPtoB tomato-interacting protein, Bti6, encoding a putative lactate dehydrogenase was used as a positive control (Xiao, et al. 2007). (C) Immunoblot analysis with anti-HA antibody in the bottom panel shows similar expression in yeast of wild-type AvrPtoB1-307 and the variant proteins from the prey vector.