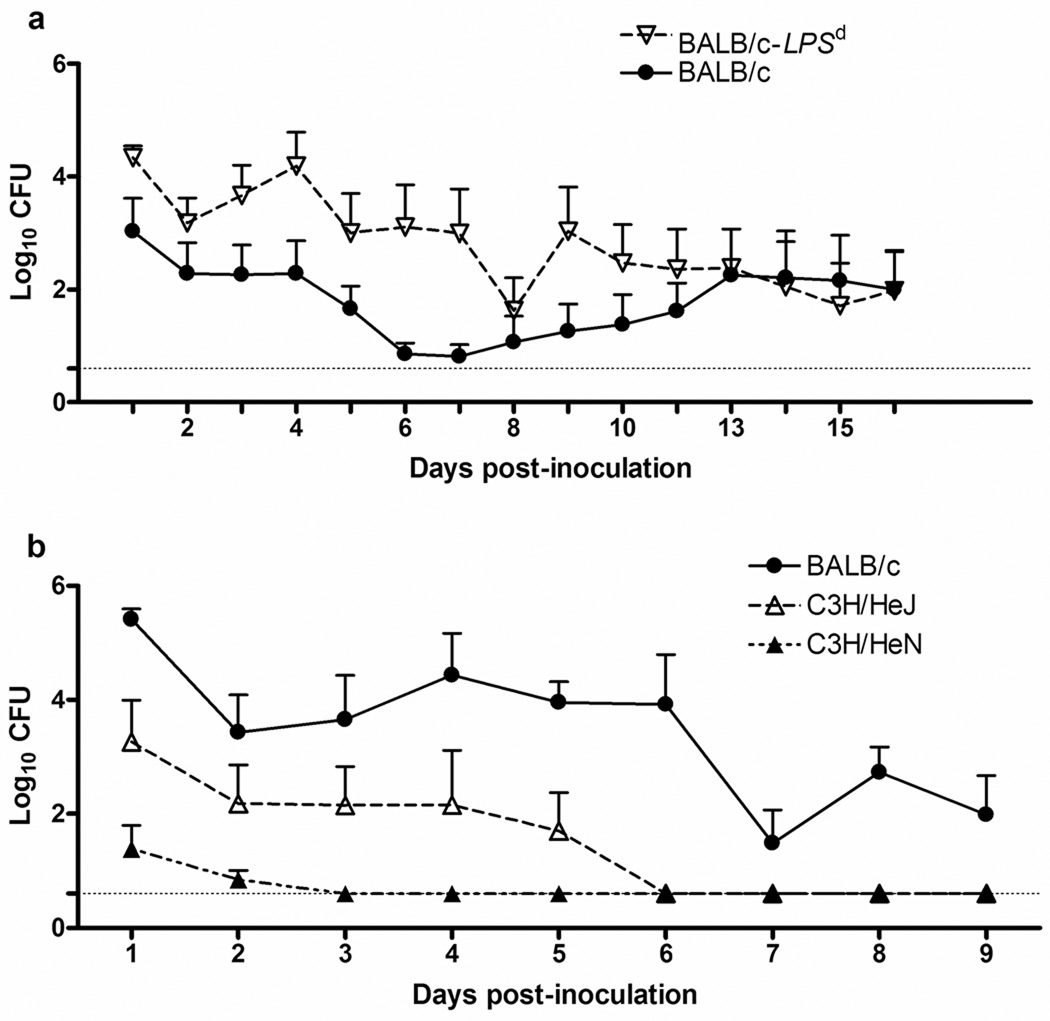
FIG. 1. TLR4 controls gonococcal colonization load in both susceptible BALB/c mice and resistant C3H mice.
Mice were inoculated intravaginally with strain FA1090 or PBS as described in the text. The recovery of gonococci from wild type or congenic mutant mice that are homozygous for the tlr4LPS-d/J gene (BALB/c-Lpsd) was determined and is expressed as log10 CFU per 100 µl of vaginal swab suspension (± Standard Error). (a) BALB/c (TLR4 wt; n=8) and BALB/c-Lpsd (TLR4 mutant; n=8); (b) C3H/HeN (TLR4 wt; n=7), C3H/HeJ (TLR4 mutant; n=5), and BALB/c mice (n=6). In each experiment, mice were inoculated intravaginally with 1 × 106 (Fig 1A) or 1 × 107 CFU (Fig. 1B) of N. gonorrhoeae strain FA1090 or PBS, and bacterial recovery was determined at the indicated times. Limit of detection for the assay is Log10 0.6 CFU, and is indicated by the dashed line. *, p ≤ 0.007 (panel A) and p ≤ 0.026 (panel B), as determined by a repeated measures ANOVA. These results are representative of two independent experiments with 4–6 mice per group in repeat experiments.