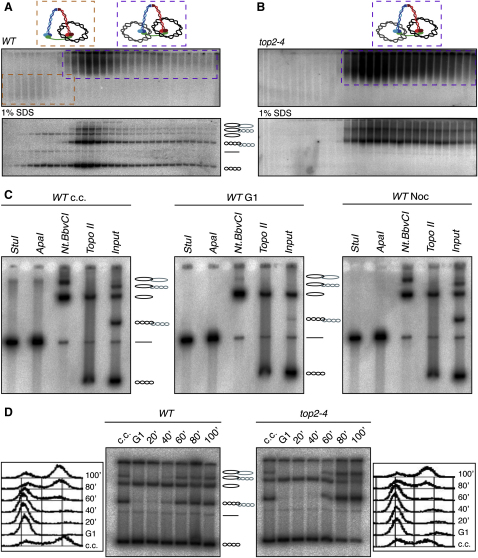
Figure 1.
Detection of Sister Chromatin Intertwining in Mitotic Cells
(A) Separation and detection by differential sedimentation and Southern blot, respectively, of monomers (dashed orange boxes) and dimers (dashed purple boxes) of large circular minichromosomes extracted from wild-type cells (K16150) grown at 25°C. Following heat denaturation in 1% SDS, the minichromosome population is resolved into six different DNA species.
(B) TOP2 protein inactivation by growth of top2-4 strain (K17890) at 37°C converts the entire minichromosome population into catenated DNAs.
(C) Identification by treatment with restriction enzymes (StuI and ApaI), nicking enzyme (Nt.BbvCI), and recombinant topoisomerase II protein (Topo II) of the six individual DNA species (from bottom upwards): supercoiled circle, linear monomer, supercoiled-supercoiled catenanes, nicked circle, nicked-supercoiled catenanes, and nicked-nicked catenanes.
(D) Documenting the formation of DNA catenanes during a cell cycle. Wild-type (K16150) and top2-4 (K17890) cells arrested with α factor pheromone were released at 37°C into rich media containing nocodazole. Time points were collected every 20 min for genomic DNA preparation and FACS.