Figure 1. Identification of a region essential for Sirt1 deacetylase activity (ESA) in the C-terminal domain.
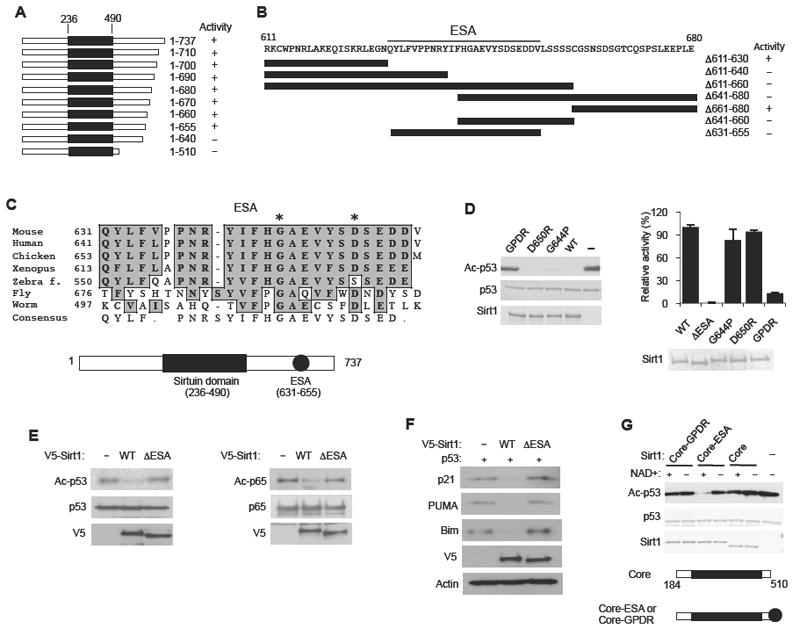
(A) A summary of the deacetylase activity of recombinant Sirt1 containing the indicated C-terminal truncations, measured by using Ac-p53 as substrate. The conserved Sirtuin domain is shown as a black rectangle. See also Figure S1A and B.
(B) A summary of the deacetylase activity of recombinant Sirt1 containing internal deletions (indicated by black bars) in the C-terminal domain. Original data for Sirt1 activity are shown in Figure S1B. The ESA region is underlined.
(C) Evolutionary conservation of the ESA region. Gly 644 and Asp 650 are indicated with asterisks (*). The locations of the Sirtuin domain and the ESA are shown below. See Figure S1C for a comparison of the C-terminal sequences of vertebrate Sirt1.
(D) Mutations of the ESA region abolish Sirt1 activity. (Left) Deacetylation reactions were performed with recombinant Sirt1 containing either a single mutation of Gly 644→Pro (G644P) or Asp 650→Arg (D650R) or a double mutation (GPDR) of these two amino acid residues. Ac-p53 is visualized by immunoblotting with an antibody specific for Ac-K382 of p53. (Right) Deacetylation reactions were performed with WT and mutant Sirt1 (including ΔESA) using 3H-Ac-H4 as the substrate. Sirt1 activity was quantified by measuring the levels of O-[3H]acetyl-ADP-ribose that was liberated from deacetylase reaction by using scintillation counting (N=4). Results are expressed as the mean ± s.e.m
(E) The ESA region is essential for Sirt1 activity in vivo. (Left) H1299 cells were transiently co-transfected with an expression vector for p53 and an expression vector for either WT Sirt1 or ΔESA Sirt1. Ac-p53 was visualized by immunoblotting with Ac-K328 (p53) antibody. (Right) Hela cells were transiently co-transfected with an expression vector for Flag-tagged NF-κB p65 (p65) and an expression vector for either V5-tagged WT Sirt1 or ΔESA Sirt1. Ac-p65 was visualized by immunoblotting with anti-Ac-Lys antibody after immunoprecipitating with Flag antibody. Transfection with an empty vector (-) was used as a negative control.
(F) Sirt1-mediated suppression of p53 activity requires the ESA region. The expression levels of p53 activated genes p21, PUMA and Bim were visualized in H1299 cells co-transfected with an expression vector for p53 and an expression vector for either WT Sirt1 or ΔESA Sirt1. Transfection with an empty vector (-) was used as a control.
(G) The ESA region is sufficient to confer activity to the decetylase core. Deacetylation reactions were performed with recombinant deacetylase core (Core, a.a. 184-510), which includes additional sequences flanking the conserved Sirtuin domain (a.a. 236-490), as well as recombinant deacetylase core fused either to the ESA region (Core-ESA) or to the ESA region containing the GPDR double mutation (Core-GPDR).
