Figure 1. Laser ablation efficiency.
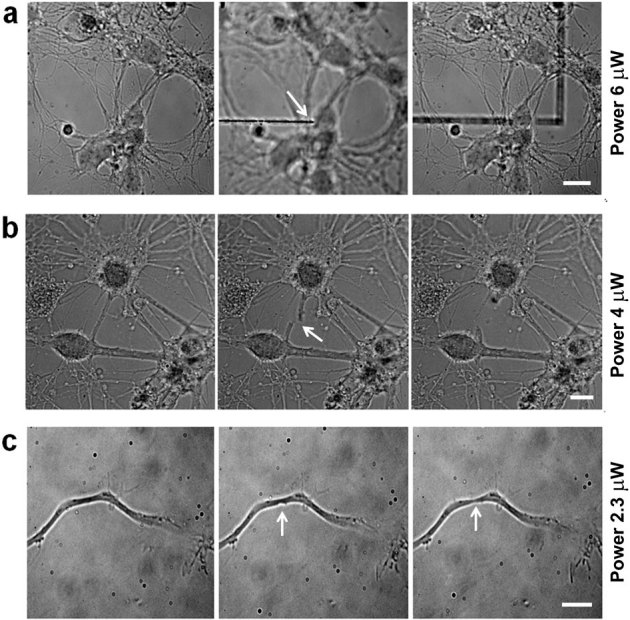
(a) Mouse hippocampal neurons were plated on a glass support, and images were taken in bright field. Neural network at 10 DIV in focus (left frame). The focus was then moved 2 μm below the cells, and with an average power of 6 μW, the glass support was ablated (middle frame) without affecting the network structure (right frame). The white arrow indicates the position of the UVA laser spot. Bar is 10 μm. (b) With an average power of 4 μW at the sample, a neural connection is completely transected (middle frame, arrow) and subsequently retracts without affecting the neighboring neurites (right frame). The white arrow indicates the transected neurite. Bar is 7 μm. (c) With an average power at the sample of 2.3 μW, the axon of a 3 DIV neuron is partially damaged without disruption of the membrane. The white arrows indicate the ablation site (middle frame) and the formation of a neck (right frame). Bar is 5 μm.
