Figure 4. (A) Unrooted phylogenetic tree based on the amino acid sequences of identified and putative GpgPs/MpgPs (EC 3.1.3.70), PGMs (EC 5.4.2.1) and of other enzymes of the histidine phosphatase superfamily.
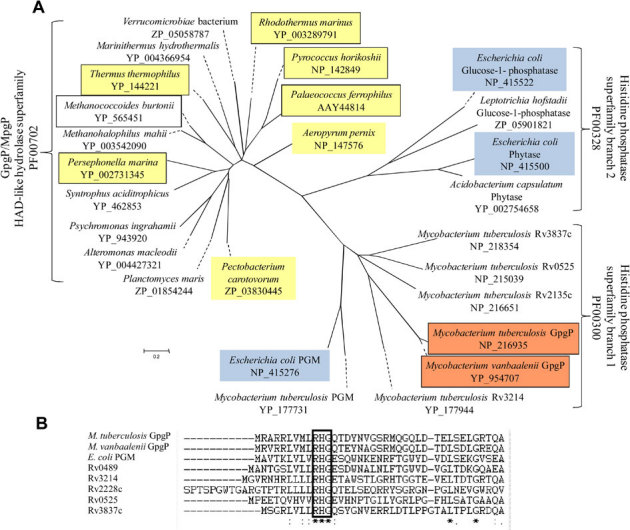
Organisms where GG (or MG) has been detected are shaded in yellow. Organisms with enzymes shown to dephosphorylate GPG (or MPG) are boxed. E. coli enzymes with confirmed function are highlighted in blue. The mycobacterial GpgPs studied in this work are highlighted in red. Peptide accession numbers (NCBI) are indicated. Scale bar, 0.2 changes per site. (B) Alignment of the N-terminal amino acid sequences of the PGM from E. coli, the GpgPs from M. vanbaalenii (Mvan_3924) and from M. tuberculosis (Rv2419c) and its paralogs. The typical “RHG” motif of the histidine phosphatase superfamily is boxed.
