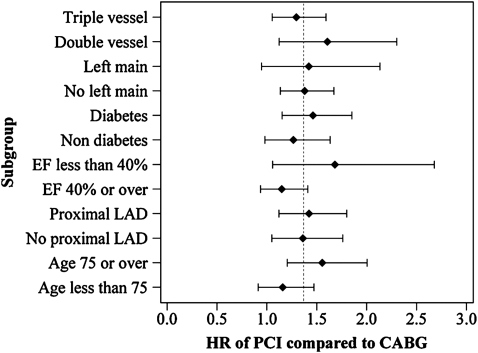
Figure 2:
Forest plot of propensity-score-adjusted hazard ratios for death after PCI as compared with that after CABG in subgroups. Dashed line indicates hazard ratio in all patients of 1.37. Interaction tests, which are design to detect whether the specific factor modifies the effect of PCI relative to CABG, were significant for age (p = 0.04) and borderline for ejection fraction (p = 0.09). These indicate that CABG is associated with better survival outcomes than PCI particularly in patients with the age of ≥75 and possibly in patients with LVEF of <40%.The other interaction tests were not significant.