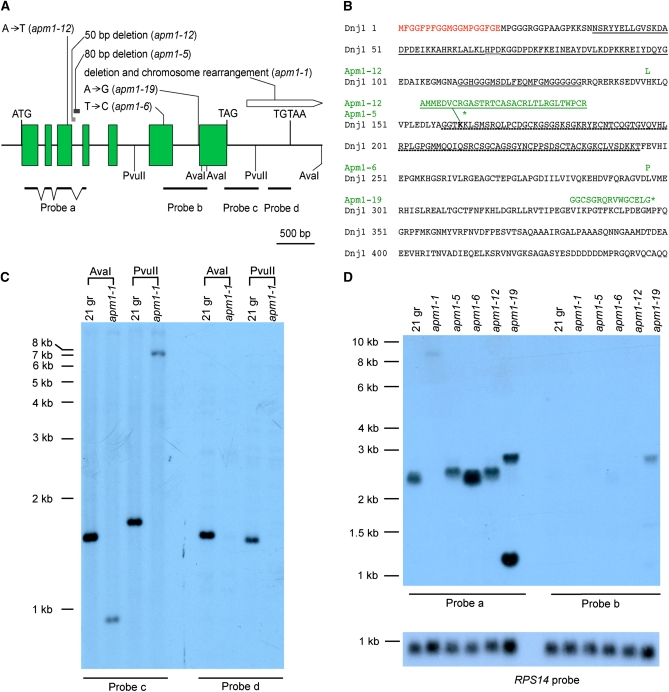
Figure 1 .
Lesions in APM1 mutant alleles affecting transcript abundance and amino acid sequence. (A) The APM1 gene contains seven exons (green rectangles) and untranslated sequences (introns and UTRs, solid line). The translation start codon ATG, termination codon TAG, and polyadenylation site TGTAA are labeled. Nucleotide deletions in alleles apm1-5 and apm1-12 are shown as gray rectangles. Nucleotide deletion and possible chromosome rearrangement in apm1-1 is drawn as a pointed white box. Positions of hybridization probes a, b, c, and d are shown. Probe a was amplified from cDNA sequence as shown by broken lines indicating exons. Only AvaI and PvuII sites generating fragments that hybridized to probes c and d are shown. (B) The amino acid sequence of the Dnj1/Hsp40 protein encoded by the APM1 gene is shown with the 19 amino acid N-terminal extension (red), the J domain (single underline), the G/F-enriched domain (double underline), and the zinc finger domain (dotted underline). Amino acid sequence alterations in individual mutant alleles are marked in green above the wild-type sequence, with corresponding allele names on the left. The Apm1-12 protein has two mutations, H124L and a 31-amino-acid (single underlined in green) replacement of K163 (boldface type); the Apm1-5 protein has a premature stop codon at K164 (*); the Apm1-6 protein changes L297P. The failure of splicing intron 6 in apm1-19 changes the reading frame and causes a premature stop codon (*). (C) Autoradiograph of Southern blot showing the deletion in apm1-1. (Left) Genomic DNA (3 mg) from wt 21gr or apm1-1 strains was digested with AvaI or PvuII and hybridized with probe c. (Right) Duplicate blot of DNA hybridized to probe d. (D) Autoradiograph of RNA blot showing DNAJ1 transcripts in wild-type and mutant strains. Total RNA (22 mg) was loaded in each lane. (Left) Transcripts hybridizing to probe a. (Right) Duplicate blot hybridized to probe b targeting intron 6. (Bottom) Labeled probe for the RPS14 gene encoding ribosomal protein S14 was used as loading control (Nelson et al. 1994).