Figure 2 .
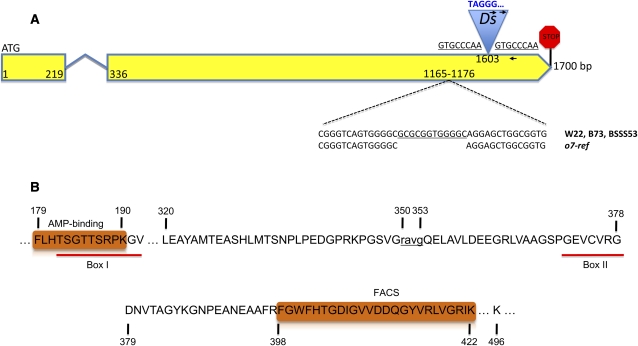
The gene structure of o7 and the important features of its protein resemble an ACS-like enzyme. (A) The 1700-bp gene is depicted as two yellow exons connected by a short intron. The positions of the o7-ref and o7-6 alleles are marked on the second exon, with the zoomed-in figure showing the 12-bp deletion of o7-ref (bottom) and the Ds insertion that generated the underlined target site duplication. The 5′ end of the Ds is colored blue, the first nucleotide being T—a distinctive feature of Ds vs. Ac elements. The two right-oriented arrows represent the two Ac/Ds-anchored primers that were paired with the gene-anchored primer (left-oriented arrow) in identifying o7-6. Their sequences are listed in Table S1. (B) The two key motifs making O7 an ACS enzyme are depicted as orange rectangles. The important residues in the 527-amino-acid protein are marked. The 4-amino-acid deletion of o7-ref is indicated in lowercase.