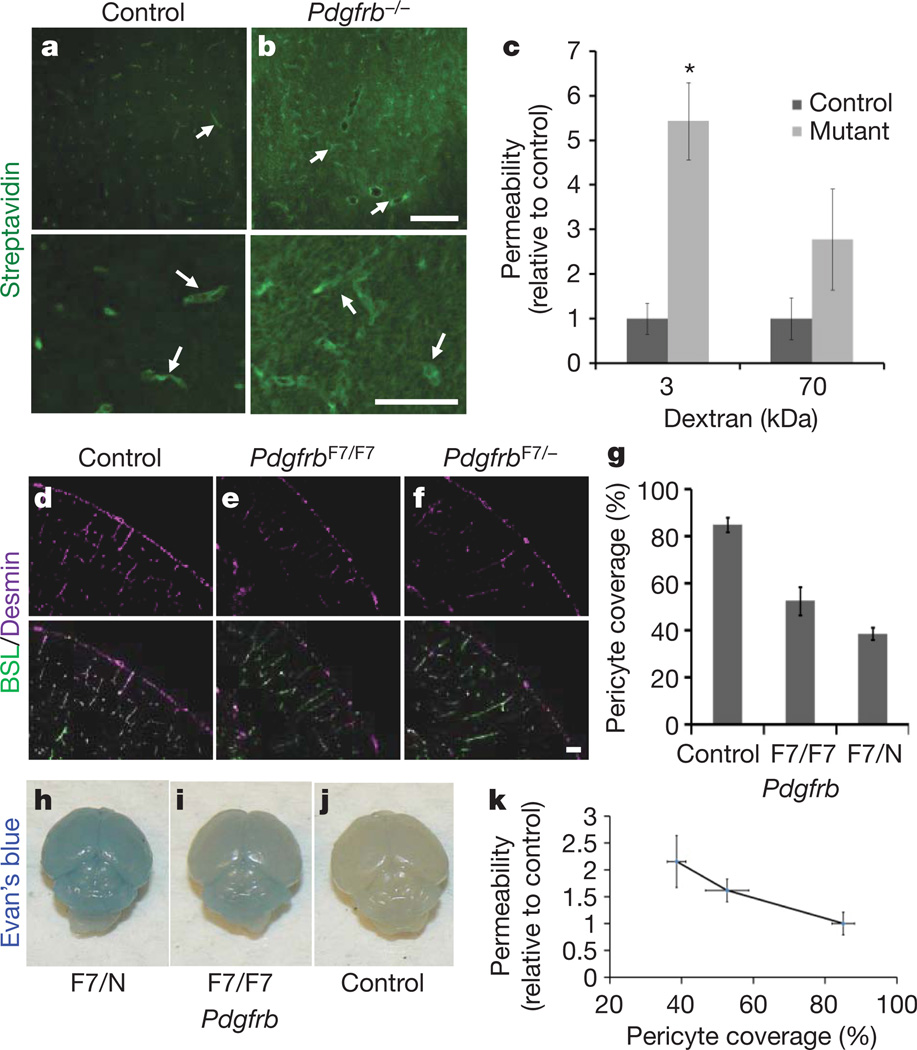
Figure 2. Pericytes are required for BBB formation.
a, b, E18 Pdgfrb−/− mice (b) and littermate controls (a) were given a trans-cardiac perfusion of biotin, and tissue sections were stained with streptavidin (green; white arrows indicate tracer in vessels). Scale bars represent 200 µm (upper panel) and 100 µm (lower panel). c, E18 Pdgfrb−/− mice and littermate controls were given a trans-cardiac perfusion of 3 kDa or 70 kDa biotinylated dextran, tissue sections stained with streptavidin-Alexa 488, fluorescence was quantified in ImageJ and permeability relative to control was graphed. *P < 0.05 by Student’s t-test. d–f, Neonatal mouse cerebral cortex from PdgfrbF7/− (f), PdgfrbF7/F7 (e) and littermate controls (d) were stained with BSL (green, d–f (bottom)) and for pericytes with anti-desmin (purple, d–f). Scale bar represents 100 µm. g, Pericyte coverage of CNS vessels in PdgfrbF7/−, PdgfrbF7/F7 and littermate control mice was quantified by analysing per cent length of BSL+ vessels opposed to desmin+ pericytes. h–j, P5 PdgfrbF7− mice (h), PdgfrbF7/F7 mice (i) and littermate controls (j) were given an intraperitoneal injection of Evan’s blue dye, and their brains were dissected the following day after PBS perfusion. k, Neonatal PdgfrbF7/−, PdgfrbF7/F7 and littermate controls were given a trans-cardiac perfusion of biotin and leakage was quantified in tissue sections with streptavidin-Alexa-488 (y axis) and graphed versus pericyte coverage (x axis; values from panel g). All error bars represent s.e.m.