Abstract
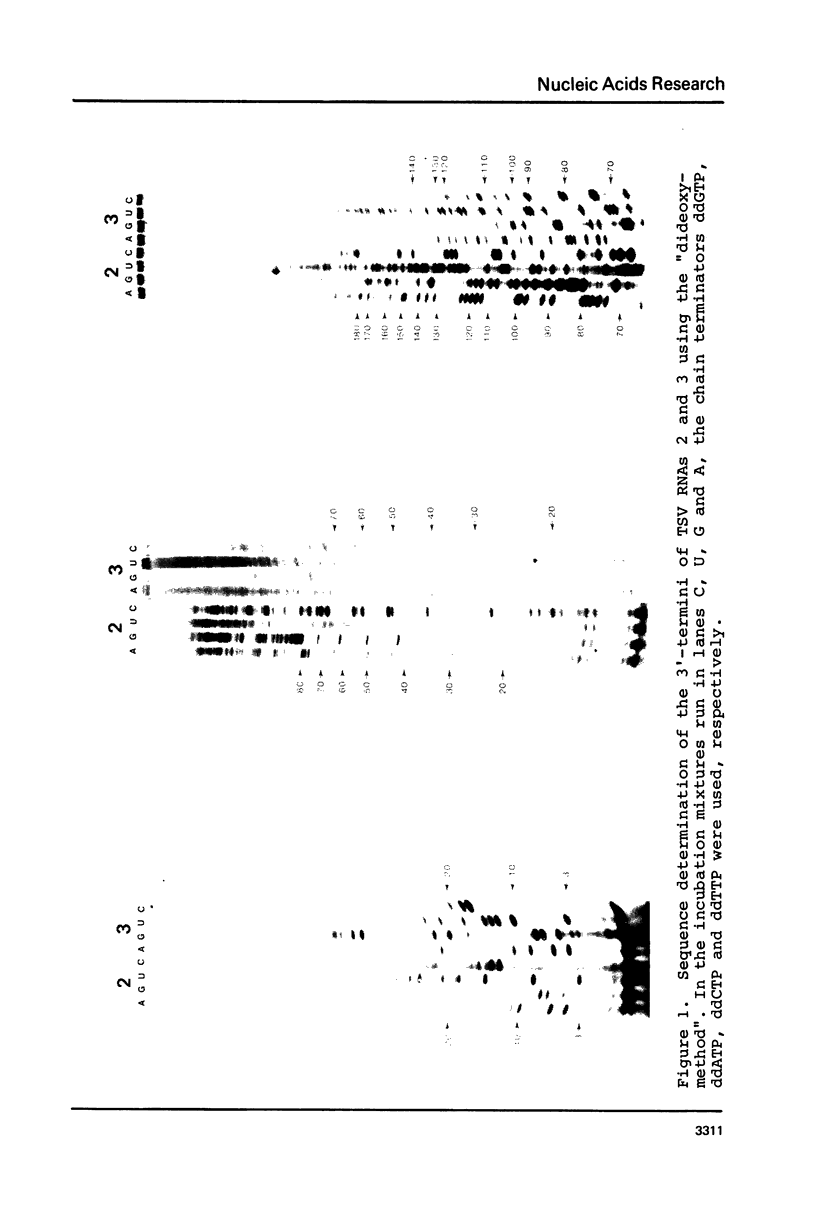
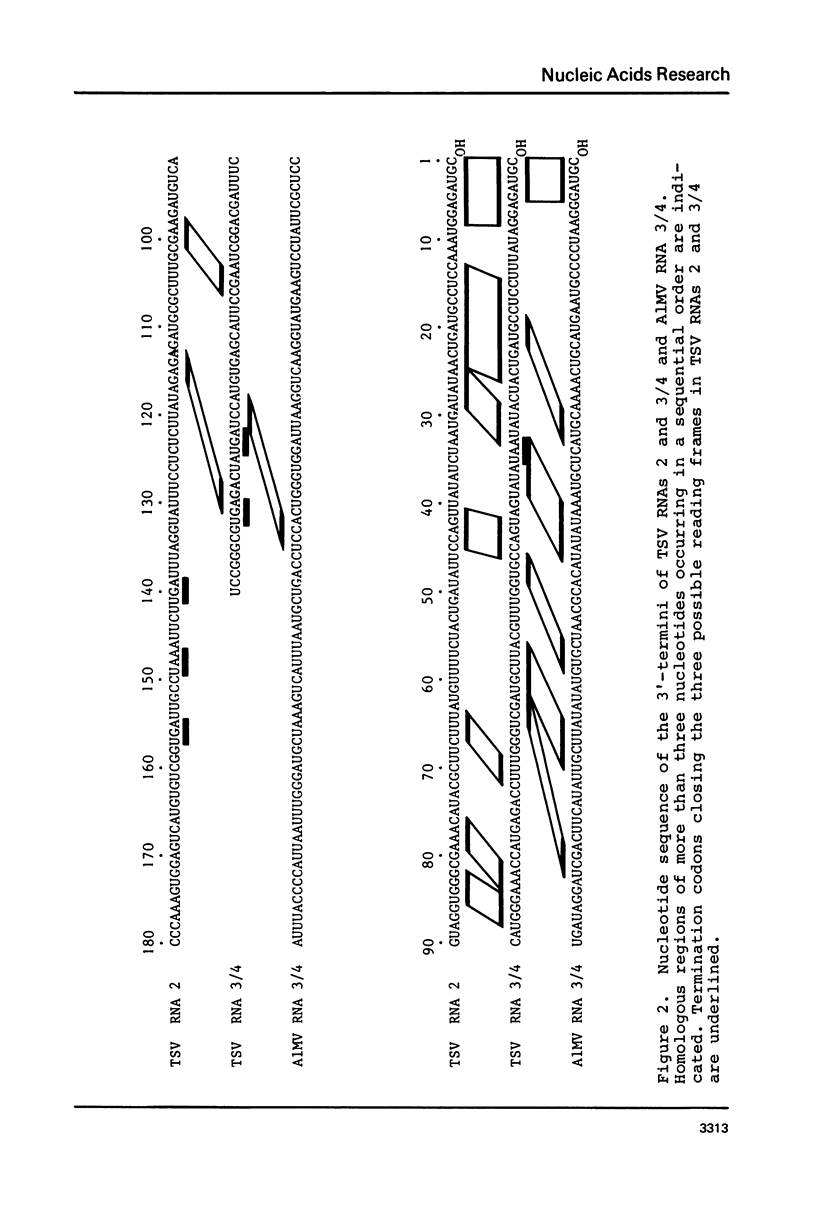
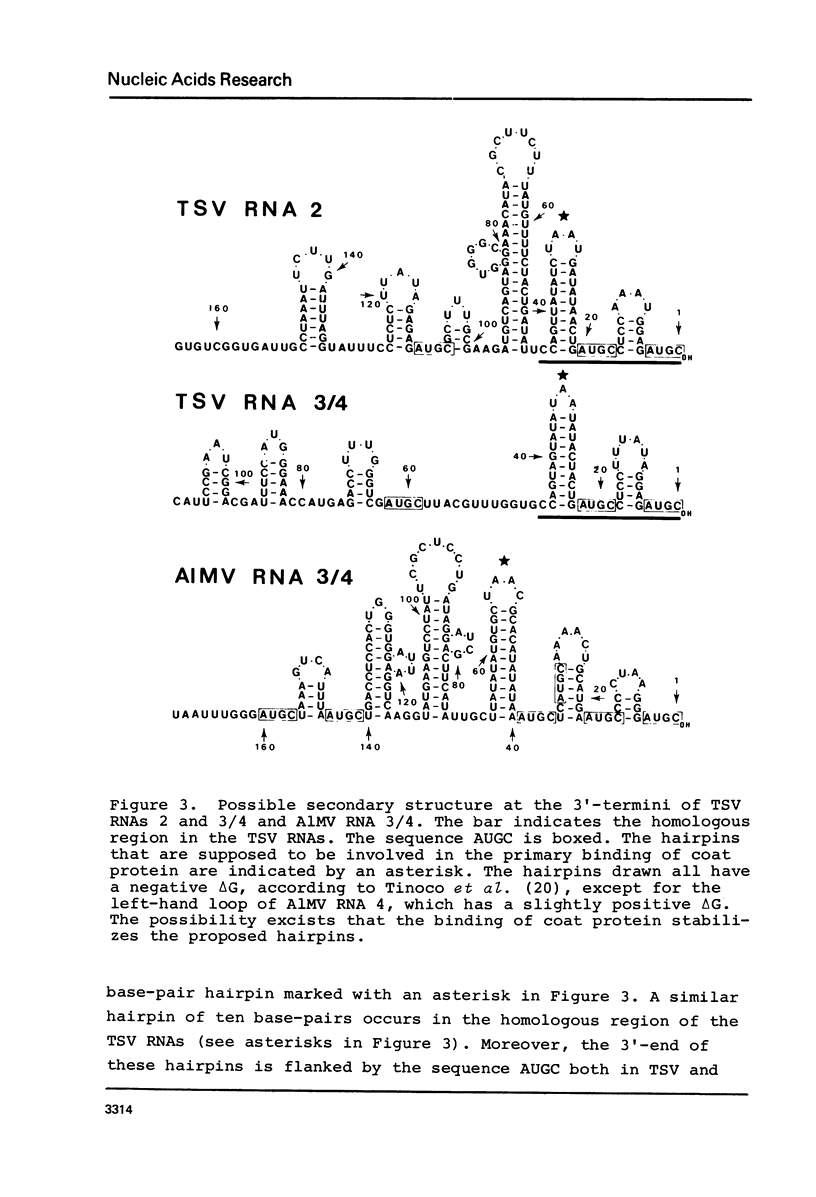
The sequence of the 3'-terminal 180 and 140 nucleotides of RNAs 2 and 3, respectively, of tobacco streak virus (TSV) was deduced by reverse transcription in the presence of a specific primer and chain terminators. Homology between the two RNAs was found to be restricted to a 3-terminal region of about 45 nucleotides. The data were compared with the sequence of the homologous region of 145 nucleotides occurring at the 3'-termini of the alfalfa mosaic virus (A1MV) RNAs, which contains the specific binding site for coat protein (Koper-Zwarthoff et al., Nucleic Acids Res. 7, 1887-1900 (1979); Houwing and Jaspars, Biochemistry 17, 2927-2933 (1978)). This was done because of the evidence that the RNAs of A1MV and TSV contain specific binding sites for their own as well as each others coat protein, and that binding of coat protein to these sites is required to initiate infection (Van Vloten-Doting, Virology 65, 215-225 (1975)). The 3'-terminal homologous regions of A1MV and TSV have two features in common: the presence of several stable hairpins and the multiple occurrence of the tetranucleotide sequence AUGC. The hairpins cause the linear array of tandemly repeated AUGC-boxes. It is postulated that the primary interaction of coat protein molecules with the RNAs of AlMV and TSV is a cooperative process involving several binding sites each being composed of a hairpin flanked at its 3'-side by an AUGC-sequence.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bol J. F., Brederode F. T., Janze G. C., Rauh D. K. Studies on sequence homology between the RNA's of alfalfa mosaic virus. Virology. 1975 May;65(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta R., Kaesberg P. Sequence of an oligonucleotide derived from the 3' end of each of the four brome mosaic viral RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4900–4904. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. W., Stanley J., Van Kammen A. Sequence homology adjacent to the 3' terminal poly(A) of cowpea mosaic virus RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Sep 25;7(2):493–500. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.2.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonsalves D., Garnsey S. M. Infectivity of heterologous RNA-protein mixtures from alfalfa mosaic, citrus leaf rugose, citrus variegation, and tobacco streak viruses. Virology. 1975 Oct;67(2):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90433-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunn M. R., Symons R. H. Sequence homology at the 3'-termini of the four RNAs of alfalfa mosaic virus. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jan 1;109(1):145–150. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81330-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall T. C., Wepprich R. K. Functional possibilities for aminoacylation of viral RNA in transcription and translation. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1976 Jan;127A(1):143–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houwing C. J., Jaspars E. M. Coat protein binds to the 3'-terminal part of RNA 4 of alfalfa mosaic virus. Biochemistry. 1978 Jul 11;17(14):2927–2933. doi: 10.1021/bi00607a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koper-Zwarthoff E. C., Brederode F. T., Walstra P., Bol J. F. Nucleotide sequence of the 3'-noncoding region of alfalfa mosaic virus RNA 4 and its homology with the genomic RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 11;7(7):1887–1900. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.7.1887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Ptashne M., Backman K., Kield D., Flashman S., Jeffrey A., Maurer R. Recognition sequences of repressor and polymerase in the operators of bacteriophage lambda. Cell. 1975 Jun;5(2):109–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews R. E. Third report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Classification and nomenclature of viruses. Intervirology. 1979;12(3-5):129–296. doi: 10.1159/000149081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellema J. E., van den Berg H. J. The quaternary structure of alfalfa mosaic virus. J Supramol Struct. 1974;2(1):17–31. doi: 10.1002/jss.400020104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinck L., Pinck M. Sequence homology at the 3'-ends of alfalfa mosaic virus RNAs. FEBS Lett. 1979 Nov 1;107(1):61–65. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80463-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. S. 5' and 3' terminal nucleotide sequences of the RNA genome segments of influenza virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 24;6(12):3745–3757. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.12.3745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symons R. H. Extensive sequence homology at the 3'-termini of the four RNAs of cucumber mosaic virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Oct 25;7(4):825–837. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.4.825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. The binding site on SV40 DNA for a T antigen-related protein. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):165–179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Vloten-Doting L., Jaspars E. M. The uncoating of alfalfa mosaic virus by its own RNA. Virology. 1972 Jun;48(3):699–708. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90154-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Vloten-Doting L. Coat protein is required for infectivity of tobacco streak virus: biological equivalence of the coat proteins of tobacco streak and alfalfa mosaic viruses. Virology. 1975 May;65(1):215–225. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



