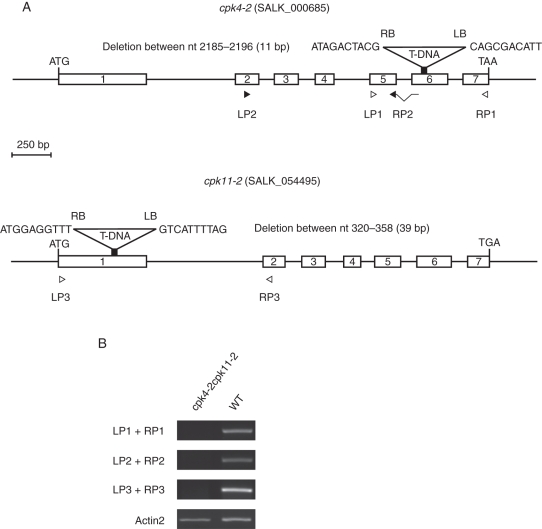
Fig. 7.
Characterization of cpk4-2 cpk11-2 mutant plants. (A) Cartoon showing genomic DNA of CPK4 and CPK11 and the T-DNA insertion sites of the corresponding mutant alleles. White boxes represent exons. Arrowheads show primer locations used for RT-PCR experiments shown in (B). The T-DNA insertion site of the cpk4-2 allele was localized in the 6th exon at nucleotide 2184 after ATG by sequencing. In the cpk4-2 mutant, 11 nucleotides (2185–2196) are deleted. The T-DNA insertion of cpk11-2 in the first exon corresponds to that published by Zhu et al. (2007) and was confirmed. (B) RT-PCR analysis of complementary DNA prepared from mutant and wild-type plant RNA revealed that in both, cpk4-2 and the cpk11-2 mutant plants no transcripts were detected (35 PCR cycles). Loading control was Actin2 (23 PCR cycles).