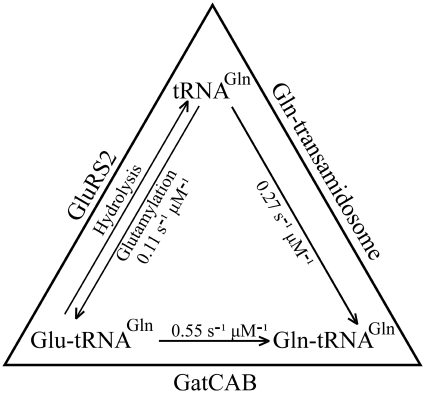
Figure 7.
A dynamic system for Gln-tRNAGln synthesis, which limits free Glu-tRNAGln in H. pylori. The constants shown are the kcat/KM values calculated from the data in Table 2, for GluRS2 and GatCAB as free enzymes, and for the stoechiometric mix forming the Gln-transamidosome. Starting with tRNAGln, the Gln-transamidosome pathway is favoured, with a kcat/KM value greater than that of the GluRS2 pathway. Glu-tRNAGln which is formed outside the Gln-transamidosome is susceptible to deacylation by GluRS2, or to an efficient transamidation by free GatCAB. The entire system therefore regulates against the presence of free Glu-tRNAGln.