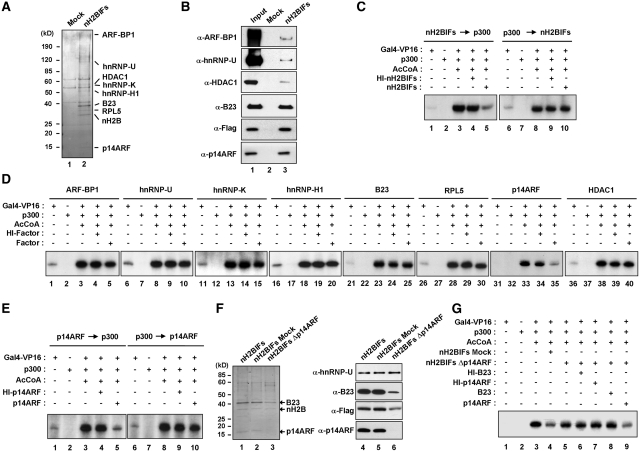
Figure 1.
Repression of chromatin transcription by p14ARF. (A) Affinity purification of nH2BIFs. Flag-HA-tagged H2B tails were stably expressed in HeLa cells and subjected to sequential immunoprecipitations utilizing anti-Flag and anti-HA antibodies. The co-purified proteins were separated by 4–20% gradient SDS–PAGE and identified by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS). The positions of the molecular mass markers (in kDa) are indicated on the left. Lane 1, mock-purified control; lane 2, nH2BIFs (H2B tail-interacting factors). (B) Immunoblot analysis of the purified nH2BIFs. The purified nH2BIFs were separated by 4–20% gradient SDS–PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Lane 1, nuclear extract input; lane 2, mock-purified control; lane 3, nH2BIFs. (C) Effects of the purified nH2BIFs on chromatin transcription. Reconstituted nucleosome arrays were transcribed in the presence of Gal4-VP16 (15 ng), p300 (20 ng), acetyl-CoA (10 µM) and/or nH2BIFs (15 ng) as summarized in Supplementary Figure S2A. The purified nH2BIFs were added before or after p300-mediated chromatin acetylation as indicated. Radiolabeled transcripts were resolved on a 5% PAGE containing 7 M urea and detected by autoradiography. Heat-inactivated tail-interacting factors (HI-nH2BIFs) were used in control reactions, and the results shown are representative of three independent experiments. (D) Effects of the recombinant nH2BIFs on chromatin transcription. Transcription reactions with G5ML601 nucleosome arrays were essentially as described in Figure 1C, but nH2BIFs were replaced by the indicated recombinant factors. Each of recombinant nH2BIFs was added prior to p300. (E) Loss of p14ARF activity upon pre-acetylation of chromatin. Transcription assays were performed under the conditions described in the legend to Figure 1D, but p14ARF was added before (lanes 1–5) or after (lanes 6–10) p300 acetylation reactions. (F) Depletion of p14ARF from the purified nH2BIFs. The purified nH2BIFs were immunodepleted of p14ARF as described in the ‘Materials and Methods’ section. To confirm that the purified factors had been depleted of p14ARF, mock- and p14ARF-depletion reactions were analyzed by Coomassie blue staining (lanes 1–3) and immunoblotting (lanes 4–6). (G) Effects of the p14ARF-depleted nH2BIFs on chromatin transcription. In vitro transcription was conducted as described in Figure 1D, except that mock-depleted (lane 4) or p14ARF-depleted (lanes 5–9) nH2BIFs were used as indicated. The p14ARF-depleted nH2BIFs were supplemented with either recombinant B23 (lane 8) or p14ARF (lane 9). Heat-inactivated (HI) B23 and p14ARF were used in control reactions (lanes 6 and 7).