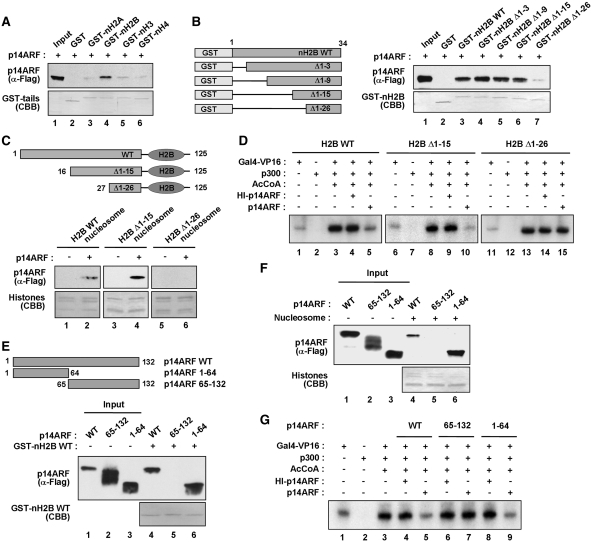
Figure 2.
Mapping of the H2B and p14ARF interaction domains. (A) Preferential binding of p14ARF to H2B tail. Interaction of 14ARF with histone tails was examined by GST pull-down assays using GST (lane 2) or GST–histone tail fusions (lanes 3–6), and the binding reactions were analyzed by immunoblotting and Coomassie brilliant blue (CBB) staining. Lane 1 contains 50% of the input p14ARF. (B) p14ARF interaction with H2B tail deletion mutants. The left panel shows the schematic illustration of H2B tail and its deletion mutants. Numbers indicate amino acid residues. The right panel shows the detection of Flag-p14ARF in GST-pull down assays with GST (lane 2) or GST-H2B tail deletion mutants (lanes 3–7). (C) p14ARF interaction with H2B tail-deleted nucleosomes. Nucleosomes containing wild-type or tailless H2B were reconstituted on biotinylated 207 bp 601 fragments and immobilized on Streptavidin agarose beads. The binding assays were performed with Flag-p14ARF, and the presence of p14ARF in the beads was analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-Flag antibody. (D) Impairment of p14ARF-induced chromatin repression by H2B tail deletions. In vitro transcription experiments were performed as described in Figure 1D, but with chromatin templates containing H2B N-terminal deletion mutants. (E) H2B tail interaction with p14ARF deletion mutants. The top panel shows the schematic illustration of p14ARF deletion mutants. The bottom panel shows the detection of p14ARF deletion mutants in GST pull-down assay with GST–H2B tail. Numbers indicate amino acid residues. Input lanes 1–3 represent 25% of p14ARF used in the binding reactions. (F) Nucleosome interaction with p14ARF deletion mutants. Nucleosomes containing wild-type H2B were reconstituted on biotinylated 207 bp 601 sequences and immobilized on Streptavidin agarose beads. The binding assays were performed with Flag-p14ARF deletion mutants, and the presence of p14ARF deletion mutants in the beads was analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-Flag antibody. (G) Effects of N- and C-terminal regions of p14ARF on chromatin transcription. Transcription reactions were essentially as described in Figure 1D, but contained p14ARF deletion mutants. Heat-treated (HI) p14ARF proteins were also tested in control reactions.