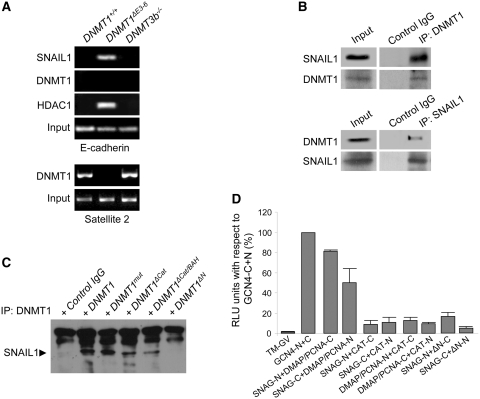
Figure 5.
The DMAP and PCNA domains of DNMT1 are required to interact with SNAIL1 and can regulate the association of SNAIL1 with the E-cadherin promoter. (A) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis of the interaction of SNAIL1, DNMT1 and HDAC1 with the E-cadherin promoter in HCT116 DNMT1+/+, DNMT1ΔE3−6 and DNMT3b−/− cells, showing strong association of SNAIL1 and HDAC1 specifically in DNMT1ΔE3−6 cells. Association of DNMT1 with Satellite 2 repetitive sequences (lower panels) was used as control. Results are representative of two experiments. (B) Coimmunoprecipitation analysis showing the interaction of SNAIL1 and DNMT1 in protein extracts of HCT116 cells after independent immunoprecipitation of either endogenous DNMT1 (upper panels) or endogenous SNAIL1 (lower panels). Results are representative of three experiments. (C) Pull-down assays showing the interaction of endogenous SNAIL1 with exogenously expressed full-length DNMT1 or deletion lacking the catalytic domain (DNMT1ΔCat), the catalytic and both BAH domains (DNMT1ΔCat/BAH) or the N-terminal region encompassing DMAP and PCNA domains (DNMT1ΔN). A 1226Cys>Val substitution (DNMT1mut) in the catalytic domain was also used. Results are representative of two different experiments. (D) Demonstration of a direct interaction of the SNAG domain of SNAIL1 with the DMAP1/PCNA domains of DNMT1 by the SPLIT-TEV method. The graph shows the relative luciferase activity of different combinations of construct transfections as indicated. As a positive control for full reporter activation to compare different experiments, a combination of the N- and C-terminal regions of the TEV protease fused to the GCN4 coiled-coil region in the presence of the membrane-bound transcriptional activator GV (TM-GV) was considered as 100% luciferase activity (GCNA4-N+C). On the opposite, luciferase activity in the presence of the membrane-bound transcriptional activator GV but in the absence of TEV activity was considered as background level (TM-GV). Combinations of either N- or C-terminal constructs of the SNAG domain of SNAIL1 with either N- or C-terminal constructs of DMAP1/PCNA domains, but not with the catalytic (CAT) domain, of DNMT1 showed a significant and strong activation of the luciferase activity reporter. The mean ± SEM of three different experiments performed in triplicate is represented.