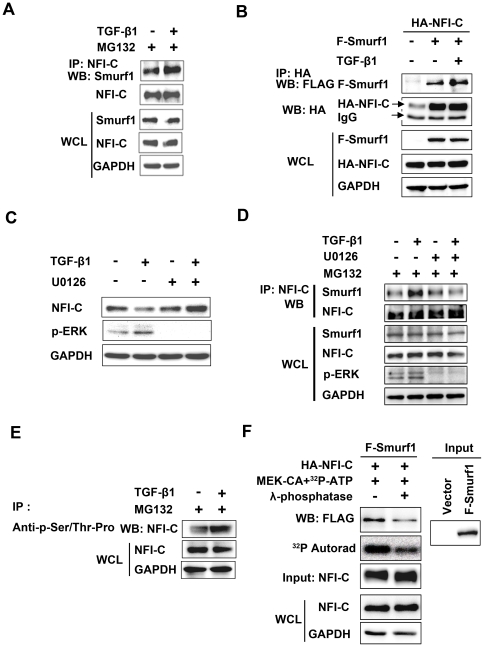
Figure 5. NFI-C interaction with Smurf1 requires activation of the MAPK pathway by TGF-β signaling.
(A) MDPC-23 cells were treated with TGF-β1 (10 ng/ml) for 1 hr and then lysed. The NFI-C immunoprecipitates or whole cell lysates (WCL) were subjected to western blot analysis with the anti-Smurf1 or anti-NFI-C antibody. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (B) HEK293T cells were co-transfected with HA-tagged NFI-C and FLAG-tagged Smurf1 expression vectors for 48 hr. WCL and NFI-C immunoprecipitates were analyzed by western blot with anti-FLAG or anti-HA antibody. (C) MDPC-23 cells were incubated with TGF-β1 (1 hr, 10 ng/ml) in the presence or absence of the MEK inhibitor, U0126 (10 µM), added 1 hr prior to TGF-β1 addition. Cells were lysed, and NFI-C, p-ERK, and GAPDH levels were analyzed by western blot. (D) MDPC-23 cells were stimulated with TGF-β1 (10 ng/ml) for 1 hr in the presence or absence of the MEK inhibitor, U0126 (10 µM). WCL and NFI-C immunoprecipitates were analyzed by western blot. (E) WCL and anti-phospho-Ser/Thr-Pro immunoprecipitates were analyzed by western blot with anti-NFI-C antibody. (F) HA-tagged NFI-C protein was metabolically labeled with [γ-32P]-ATP in HEK293T cells. Bound Smurf1 proteins were eluted from the beads and detected by western blot analysis with the indicated antibody. The incorporation of 32P was detected by autoradiography, and the amount of HA-NFI-C was detected by western blot analysis.