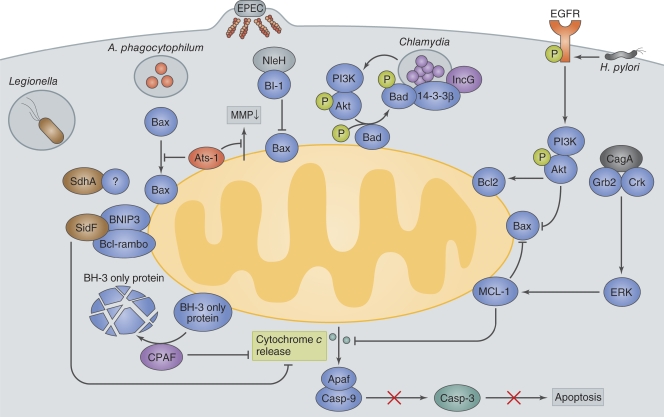
Figure 2.
Bacterial manipulation of mitochondrial cell death pathways. Legionella deliver SidF and SdhA. SidF interacts with two pro-apoptotic proteins, BNIP3 and Bcl-rambo, and inhibits apoptotic signaling. SdhA inhibits host cell death and enhances bacterial survival and replication by an as yet unknown mechanism. A. phagocytophilum delivers Ats-1 and prevents the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) and Bax translocation to the mitochondria to inhibit apoptosis. EPEC delivers NleH, which interacts with Bax inhibitor 1 (BI-1) and blocks epithelial apoptosis. Chlamydia secrete CPAF, which degrades the pro-apoptotic BH3-only proteins, thereby blocking the release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria. Chlamydia infection also inhibits the function of the pro-apoptotic protein Bad by causing its phosphorylation by Akt and mislocalization to Chlamydia inclusion vacuoles via its interaction with 14-3-3β and IncG. H. pylori delivers the T4SS effector CagA to attenuate epithelial cell apoptosis. The CagA and Grb2 or Crk interaction stimulates the ERK1/2 pathway and up-regulates the production of the anti-apoptotic factor MCL-1. H. pylori activates EGFR, thereby up-regulating anti-apoptotic signaling involving Akt and Bcl2.