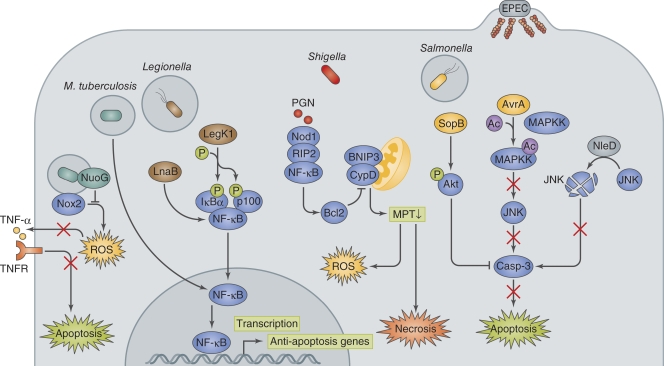
Figure 3.
Bacterial manipulation of host pro-survival pathway. M. tuberculosis activates host anti-apoptotic signaling by up-regulating the anti-apoptosis genes Mcl-1, bfl1, and FLIP. NuoG dampens Nox2-mediated host signaling, resulting in the inhibition of apoptosis. Legionella deliver LegK1 and LnaB, which enhance the pro-survival activity of NF-κB. Shigella invasion of the epithelium results in mitochondria permeability transition (MPT)−dependent ROS production and necrosis-like cell death, which is counterbalanced by the NOD1−RIP2−NF-κB−Bcl2 pro-survival pathway. PGN, peptidoglycan. Salmonella deliver SopB and AvrA via the T3SS, and they inhibit apoptosis by activating the PI3K–Akt pro-survival pathway via inositol phosphate activity and by preventing JNK pro-cell death signaling via acetyltransferase activity, respectively. EPEC also targets JNK signaling by delivering NleD, which uses its metalloprotease activity to cleave JNK, thereby inhibiting cell death.