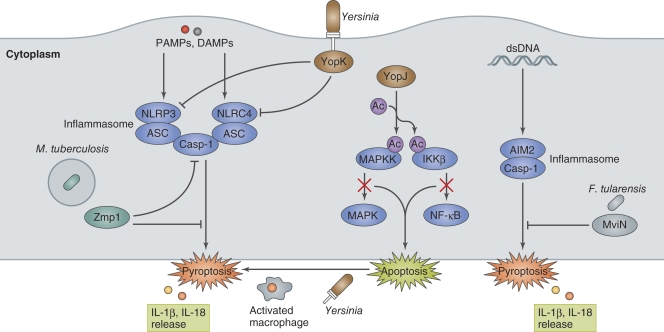
Figure 4.
Bacterial manipulation of inflammasome activation. PAMPs or DAMPs (such as dsDNA) generated by bacterial invasion and multiplication in macrophages trigger NLRP3-, NLRC4-, AIM2-inflammasome assembly and induce pyroptosis. Yersinia induce apoptosis by YopJ-mediated inhibition of pro-inflammatory signaling in the initial stage of infection in naive macrophages. Activated macrophages redirect YopJ-mediated apoptosis to YopJ-independent pyroptosis. However, Yersinia prevent inflammasome activation by secreting YopK, which interferes with T3SS recognition by NLRP3 and NLRC4. M. tuberculosis Zmp1, a Zn metalloprotease, and F. tularensis MviN, a putative lipid II flippase, prevent inflammasome activation and IL-1β secretion/pyroptosis by unknown mechanisms.