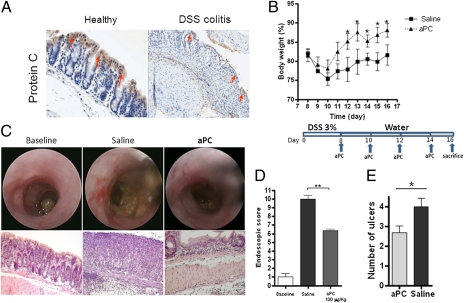
Fig. 5.
Exogenous administration of aPC ameliorates recovery of intestinal mucosa in DSS-induced colitis. (A) Immunohistochemical staining of PC on sections of colon from WT mice before and after administration of 3% DSS. Arrows indicate the strong expression of PC on ECs in healthy colon and its dramatic reduction after DSS treatment. (B) After 8 d of DSS administration, WT mice were divided into two groups: One group received saline, and the other group received recombinant murine aPC (100 μg/kg) intrarectally in a volume of 80 μL using a straight gavage needle every other day after colitis was established. Loss of body weight was monitored daily during treatment. (C and D) Endoscopic images and evaluation of mucosal damage in the colons of healthy and saline- and aPC-treated mice on day 16. (E) Evaluation of the number of ulcers on day 16 after topical aPC or saline treatment. Values are mean ± SEM; n = 6 mice for all groups. These data are representative of two independent experiments. *P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01. Images were taken using a 20× objective.