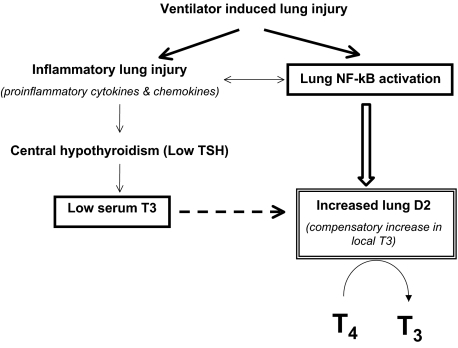
Fig. P1.
Ventilator-induced lung injury is characterized by increases in inflammatory cytokine expression and activation of mediators of immune and inflammatory responses such as NF-κB. Proinflammatory cytokines increase hypothalamic D2 and cause central hypothyroidism, which is likely responsible for the low serum levels of T3. The induction of D2 in the lung by mechanical ventilation appears to be an adaptation to the low circulating levels of T3 or may caused by to the local activation of NF-κB. The dashed arrow represents the posttranslational effect of T3 on D2.