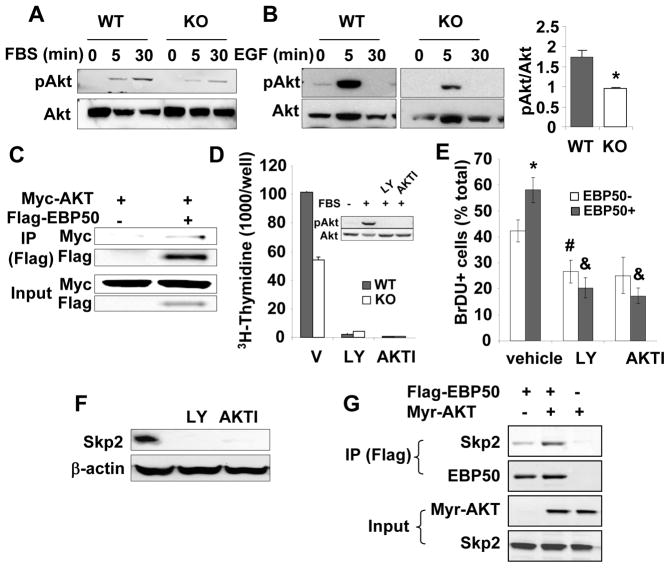
Figure 5. EBP50 ablation decreases Akt signaling and Skp2 expression.
A. WT and KO VSMC were serum-starved for 16 h followed by the addition of 10% FBS for the indicate times. Phosphorylated and total Akt were determined by immunoblotting. Blots are representative of 4 independent experiments. B. WT and KO VSMC were serum-starved for 16 h followed by the addition 10 ng/ml EGF for the indicate times. Phosphorylated and total Akt were determined by immunoblotting. Graph shows the quantitation of 3 independent experiments. *<0.05. C. Primary VSMC were transiently transfected with Myc-Akt and Flag-EBP50, as indicated. Cells were lysed, and immunoprecipitation experiments were performed with anti-Flag antibody followed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with anti-Flag or anti-Myc antibodies. D. Proliferation (determined by [3H]-thymidine incorporation) of WT and KO VSMC treated without or with 10 μM LY-294002 (LY) or 5 μM AKTI for 16 h and maintained in 10% FBS. Data are expressed as mean ± standard error for triplicate determinations. Shown is also a western blot analysis of phosphorylated and total Akt in similarly treated cells. E. Primary VSMC from KO mice were electroporated with YFP-EBP50, treated without or with 10 μM LY-294002 (LY) or 5 μM AKTI in the presence of BrDU for 16 h. Cells were fixed and stained for BrDU. The percentage of BrDU positive non-transfected and YFP-EBP50-expressing cells was determined from three independent experiments. *, p=0.03 vs. EBP50-, #, p<0.02 vs. vehicle, &, p<0.01 vs. vehicle; N=3. F. VSMC maintained in 10% FBS were treated without or with 10 μM LY-294002 (LY) or 5 μM AKTI. Skp2 expression was determined by immunoblotting. β-actin was used as loading control. G. CHO cells were transiently transfected with constitutively active HA tagged Myr-Akt and Flag-EBP50, as indicated. Cells were lysed, and immunoprecipitation experiments were performed with anti-Flag antibody followed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with anti-Flag, anti-HA or anti-Skp2 antibodies.