Figure 5. Plasma IgM and IgG binds to enteric bacteria.
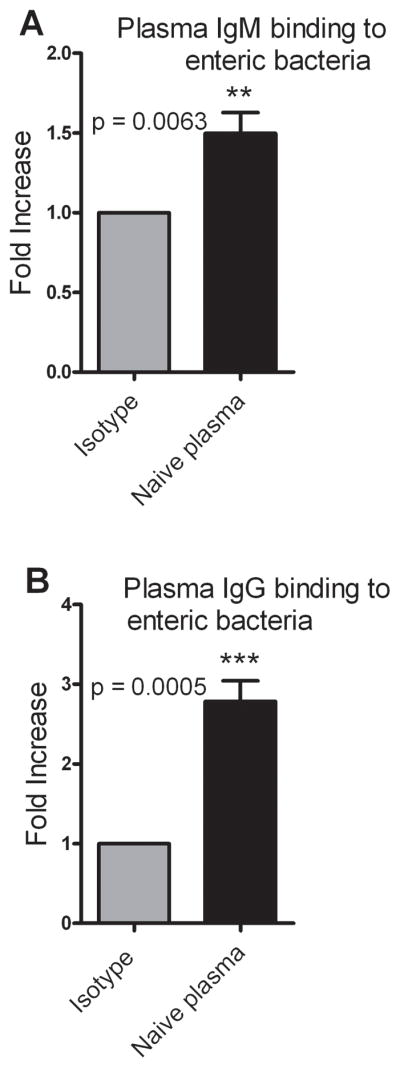
Plasma was used to opsonize enteric bacteria and the opsonized bacteria were stained with either PE anti–mouse IgM or FITC anti–mouse IgG. Isotype controls for IgM and IgG were PE Rat IgG2a, κ and FITC Rat IgG1, κ respectively. (A) Plasma IgM binding to enteric bacteria represented as a fold increase over isotype control. n = 8. (B) Plasma IgG binding of enteric bacteria represented as a fold increase over isotype control. n = 7. Data are the combined results of 3 independent experiments. p < 0.05 when compared to isotype control.
