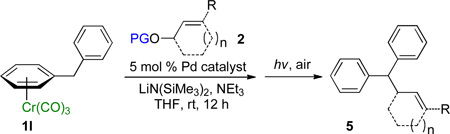
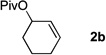
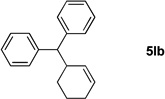
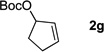
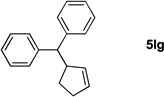
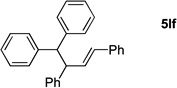
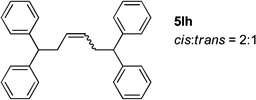
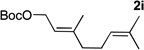
Table 4.
Tandem Synthesis of Diphenylmethane Derivatives.a
Reactions conducted on a 0.1 mmol scale using 1 equiv of 1l, an excess of LiN(SiMe3)2 and 2 at 0.1 M. (see Supporting Information for details).
Isolated yield after chromatographic purification.
Ratio of linear / branched (L:B) was determined by 1H NMR of the crude reaction mixture. The regioisomers were separable by silica gel chromatography.
[Pd(allyl)Cl]2/1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane (DPPP) was used as catalyst in place of Pd(COD)Cl2/Xantphos.