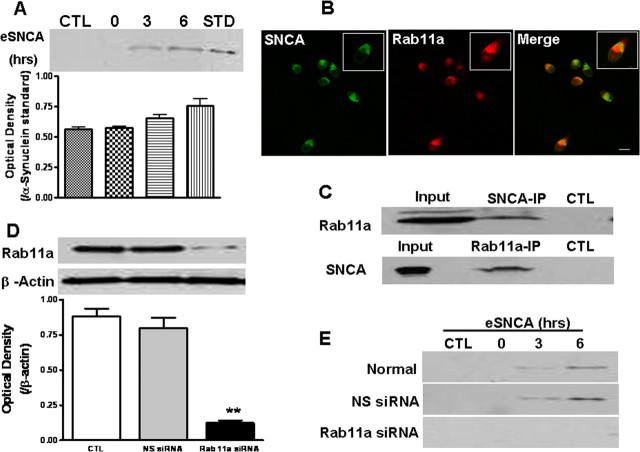
Figure 1.
Rab11a and recycling of internalized eSNCA. A, Cells were pulsed with human preaggregated eSNCA for 3 h, washed extensively with PBS followed by adding fresh serum-free medium, and then chased for various time points. At the end of the experiment, the medium was collected and eSNCA was detected at basal (CTL), 3 and 6 h after the chase, along with standard (STD) SNCA. B, MES cells, seeded at 0.05 × 106/well, were treated with fluorescent labeled eSNCA (green) at 250 nm for 3 h before chasing. At an appropriate time, cells were stained with anti-rab11a (red) antibody, followed by examination with confocal microscopy. Note: SNCA was colocalized with rab11a after chase for 3 h (yellow color seen in the insert of the merged image). C, The protein complex of interest was isolated from MES cells homogenate after chasing for 3 h. Coimmunoprecipitation analysis using magnetic beads conjugated with either SNCA (top) or rab11a (bottom) with subsequent pull-down revealed a noticeable protein–protein association between SNCA and rab11a. Input represents original materials. D, MES cells were transfected with rab11a siRNA before treatment with eSNCA. Expression levels of rab11a were analyzed by Western blotting with an anti-rab11a antibody 72 h after gene manipulation, demonstrating that rab11a siRNA effectively inhibited rab11a expression [**p < 0.01, compared with control/nonsense (NS) siRNA groups; β-actin used as loading control]. E, MES cells were transfected with rab11a siRNA before treatment with eSNCA. The amount of eSNCA in condition media was measured by Western blotting analysis with or without rab11a siRNA transfection. A significant blocking in TCA-precipitable eSNCA was found in the condition medium of MES cells transfected with rab11a at 3–6 h chasing. Scale bar, 20 μm.