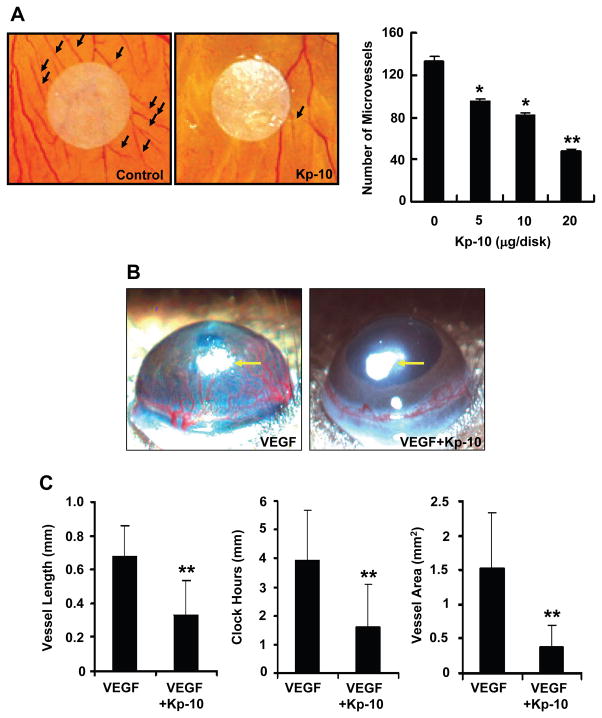
Figure 2. Inhibition of angiogenesis by Kp-10 in vivo.
(A) Kp-10 inhibits angiogenesis in chicken embryo chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) assay. Representative pictures of PBS-control and Kp-10-treated CAM, showing inhibition of new blood vessel growth (black arrows) by the treatment of different concentrations of Kp-10 within a defined area surrounding the implanted disk. *, p<0.05 and **, p<0.01. (B) Kp-10 inhibits angiogenesis using mouse corneal micropocket assay. Micropellets (yellow arrows) containing 160 ng of VEGF were implanted into corneal micropockets of C57BL/6 mice as described in materials and methods. The effects of Kp-10 on angiogenesis in vivo were examined using slow-releasing polymer containing four different treatment groups: saline alone, 1 μg Kp-10 alone, 160 ng VEGF alone, and 160 ng VEGF plus 1 μg Kp-10. Saline alone and Kp-10 alone were used as controls in the experiments. Corneal neovascularization was measured and photographed with a stereo-microscope on day 7 after implantation. Positions of pellets were pointed with arrows. (C) Kp-10 inhibited vessel length, clock hours of circumferential neovascularization, and the area of neovascularization, respectively. The bio-microscopic assessment was conducted by two independent observers. Results are given as mean ± SEM. **, p<0.01.