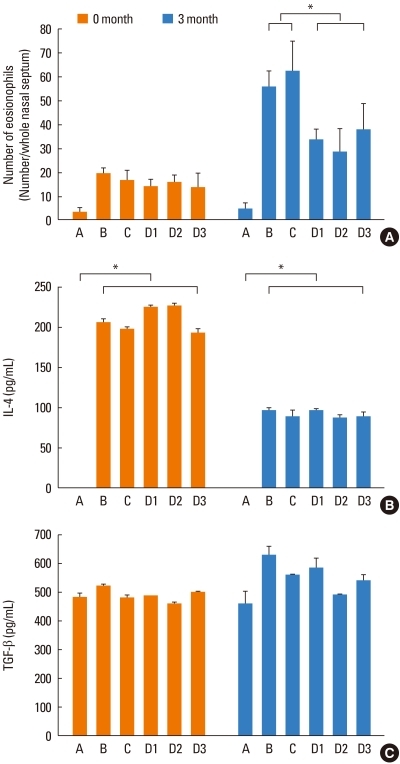
Fig. 2.
Inhalation of ovalbumin (OVA) treatment enhances eosinophil recruitment and the production of IL-4 and TGF-β. (A) Eosinophils were counted in nasal mucosa sections from mice in groups B, C, D1, D2, and D3 that were sacrificed at 0 or 3 months. (B) IL-4 production was measured in the supernatant of OVA-stimulated splenocyte cultures from mice sacrificed at 0 or 3 months. (C) TGF-β production was measured in the supernatant of OVA-stimulated splenocyte cultures from mice sacrificed at 0 or 3 months. Data are presented as the mean±SD. Group A, phosphate-buffered saline treated; group B, OVA treated; group C, dimethyl sulfoxide/OVA treated; group D1, OVA/SU1498 treated; group D2, OVA/AG1296 treated; group D3, OVA/SU1498/AG1296 treated. *P<0.05.