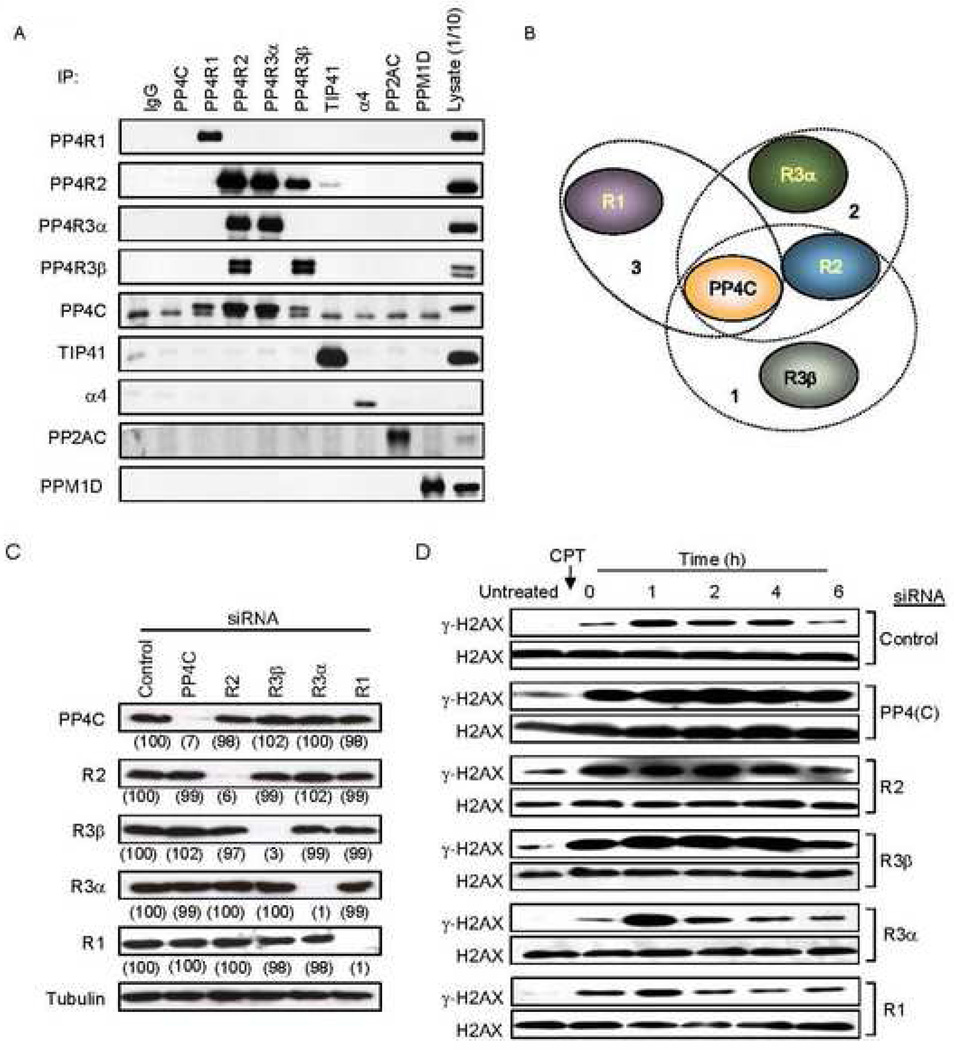
Fig. 2. Knocking down the PP4C-R2-R3β complex alters basal γ-H2AX levels.
A) Reciprocal immunoprecipitation/immunoblot of PP4 complex proteins in 293T cell lysates. The PP4C antibody worked for immunoblot, but failed to immunoprecipitate detectable amounts of PP4C. The lower band in the PP4C blot is a nonspecific cross-reacting band. The PP4 complex subunits R1, R2, R3α and R3β associated with PP4C and did not interact with the other phosphatases, PP2AC and PPM1D.
B) Schematic representation of the distinct PP4 complexes.
C) siRNAs targeting specific PP4 subunits reduce their expression without altering other PP4 subunits or tubulin. HeLa cells transfected with the indicated siRNAs were harvested after 40 h and analyzed by immunoblot. Experiments described henceforth were performed using these siRNAs. Numbers in parentheses indicate signal intensity as a percent of control.
D) Knocking down certain PP4 subunits increases basal γ-H2AX levels. Control or PP4 subunit specific siRNA-transfected HeLa cells, treated or not with CPT (2 µM, 1 h), were harvested at indicated times and whole cell extracts were probed for γ–H2AX or H2AX. PP4R3β, PP4R2 and PP4C deficient cells have increased γ-H2AX both in untreated cells and after CPT treatment.