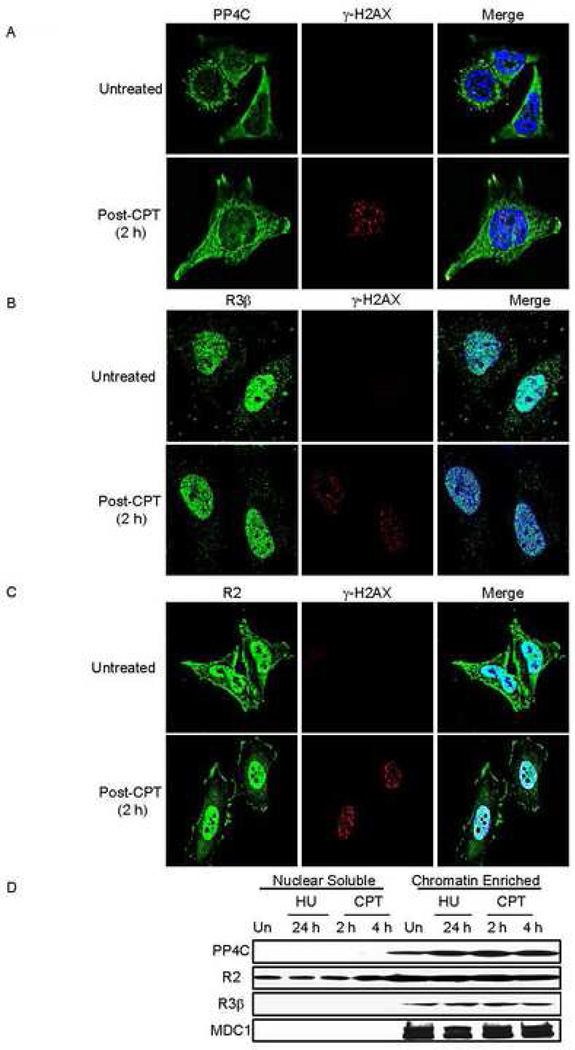
Fig. 4. Subcellular localization of PP4C, PP4R3β and PP4R2 does not substantially change in response to exogenous DNA damage.
Untreated or CPT-treated (5 µM, 1 h, 37°C) HeLa cells were washed to remove CPT and incubated for 2 h, before fixing and staining for γ–H2AX and PP4C (A), PP4R3β (B) or PP4R2 (C). Images were visualized using laser-scanning confocal microscopy. PP4C is primarily perinuclear with some nuclear staining, but PP4R3β and PP4R2 are predominantly nuclear, suggesting that the PP4C-R2-R3β complex mostly resides in the nucleus. None of these components substantially changed their localization following CPT treatment.
D) The PP4C-R2-R3β complex is associated with chromatin in fractionated nuclei from HeLa cells, treated or not with 2 mM HU for 24 h or with 10 uM CPT for 2 or 4 h. Although PP4R2 was also found in the nuclear soluble fraction, PP4C and PPR3β were exclusively detected in the chromatin fraction. MDC1 served as a control for the chromatin fraction.