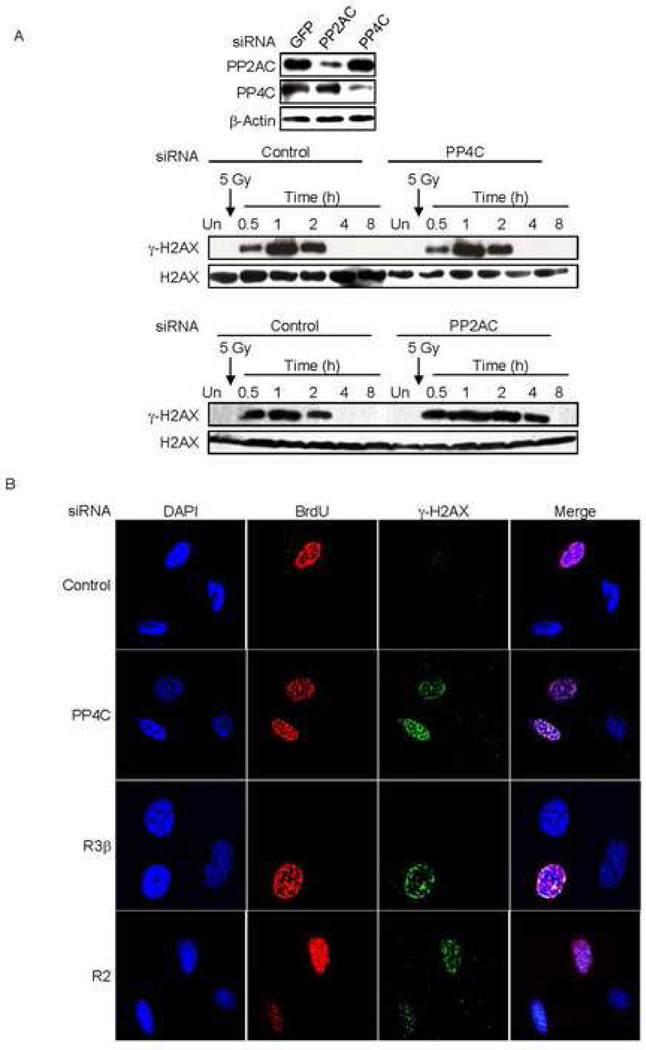
Fig. 6. γ-H2AX formation in PP4-knocked down cells is dependent on cell division.
A) Knocking down PP4C in non-dividing cells (macrophages) has no effect on γ-H2AX. Human macrophages were transfected with control siRNAs or siRNAs targeting PP2AC or PP4. Immunoblots showed significant knockdown of PP2AC and PP4C (upper panel). Macrophages in which PP4C (middle panel) or PP2AC (lower panel) were knocked down were irradiated (5 Gy) and immunoblots of whole cell extracts at indicated times probed for γ–H2AX or H2AX. Macrophages with lower amounts of PP4C showed no change in γ-H2AX relative to control cells, but γ-H2AX persisted longer in cells with reduced PP2AC.
B) γ-H2AX foci formation in PP4-deficient cells is induced by DNA replication. Serum starved 293T cells were transfected with siRNAs targeting PP4C, PP4R2 or PP4R3β. Transfected cells were released from the G0/G1 block by adding serum and BrdU was added to visualize cells that had undergone DNA replication. After 12 h, cells were washed before fixing and staining for BrdU, γ–H2AX and DAPI. Images were visualized using laser-scanning confocal microscopy. After partial depletion of PP4 complex proteins, only cells that were BrdU positive (had undergone DNA replication) showed γ-H2AX foci.