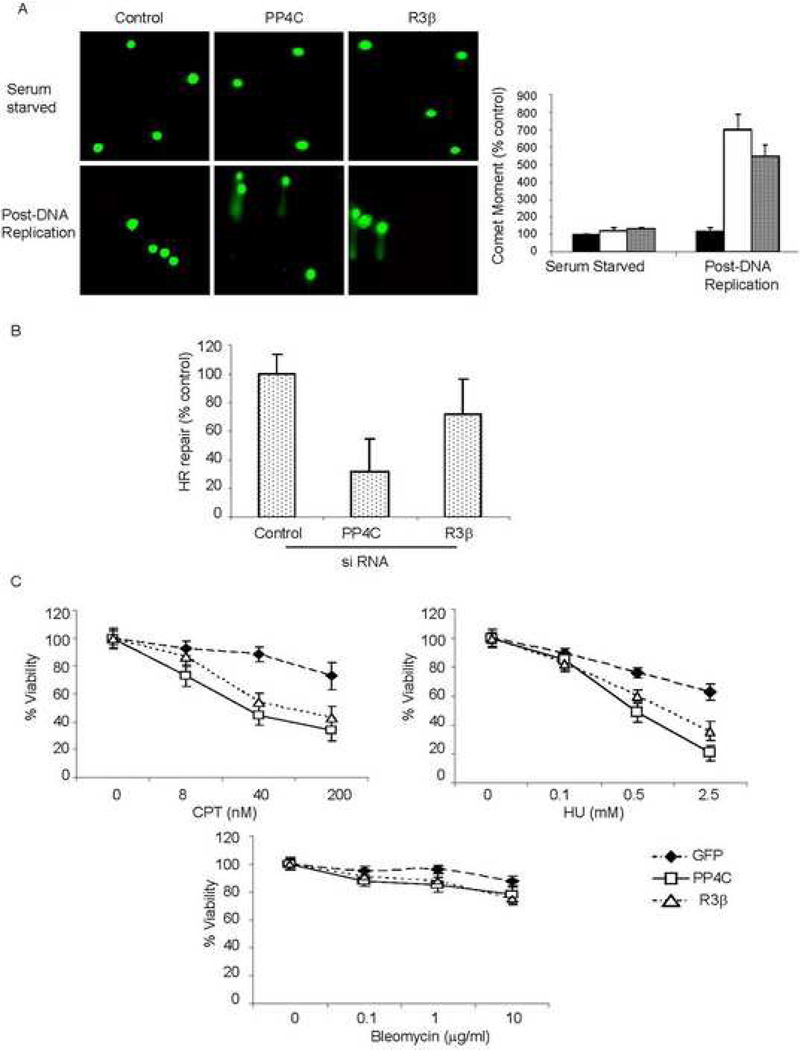
Fig. 7. PP4 is required to repair DNA replication-mediated DNA damage.
A) Knocking down the PP4 complex impairs DNA repair in dividing cells. PP4C, PP4R3β or control siRNA-transfected 293T cells were serum starved for 2 d. Cells were either mainta ined in low serum or released from G0/G1 block by adding serum and analyzed by single cell gel electrophoresis (comet assay) 12 h later. Representative images are shown above. The comet tail moment of 75 cells for each condition was quantified using NIH Image software. The comet moment was normalized to that of control cells (black bar) and expressed as a percentage. DNA damage in the PP4C (white bar, p<0.02) and R3β (dotted bar, p<0.02) deficient cells was significantly increased only after DNA replication resumed.
B) Measurement of HR-mediated repair of an I-SceI-induced DSB. U2OS cells carrying the recombination substrate (DR-GFP) were transfected with PP4C, PP4R3β or control siRNAs. I-SceI expression plasmid was transfected after 24 h and GFP+ cells measured 48 h later. HR repair was significantly impaired in cells transfected with PP4C (p<0.01) or R3β (p< 0.01) siRNA.
C) PP4-silenced cells are hypersensitive to DNA replication inhibitors. Cell viability was analyzed by MTT assay relative to untreated cells. Curves were generated from 3 independent experiments. PP4C or PP4R3β deficient cells were hypersensitive to CPT (p<0.001, left) and HU (p<0.002, right), but not to bleomycin (lower) relative to control cells.
In panels (A–C), the mean ±S.D. of representative experiments are shown.