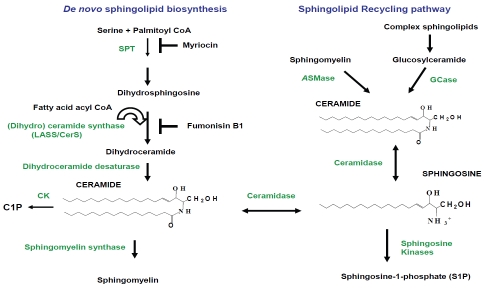
Figure 1.
Biosynthesis of ceramide and its conversion into other bioactive sphingolipids. De novo ceramide synthesis begins with the conversion of serine and fatty acyl CoA into 3-ketosphinganine by serine palmitoyl transferase (SPT), then 3-ketosphinganine is converted into dihydrosphingosine. Myriocin is a potent inhibitor of SPT activity. (Dihydro) ceramide synthase (LASS/CerS) acylates dihydrosphingosine to form dihydroceramide, which is then reduced to ceramide by dihydroceramide desaturase. Ceramide is also produced by SMases through SM degradation in SMase pathway. Ceramidase converts ceramide into sphingosine, which is phosphorylated by sphingosine kinase (SK) to generate sphingosine-1-phosphate. Ceramide is phosphorylated by ceramide kinase (CK) yielding ceramide-1-phosphate (C1P). In the salvage or recycling pathway, complex sphingolipids are broken down to ceramide by glucosylceramidase (GCase) and then by ceramidase to sphingosine, which is re-acylated to ceramide by LASS/CerS. Fumonisin B1 inhibits LASS/CerS activity.