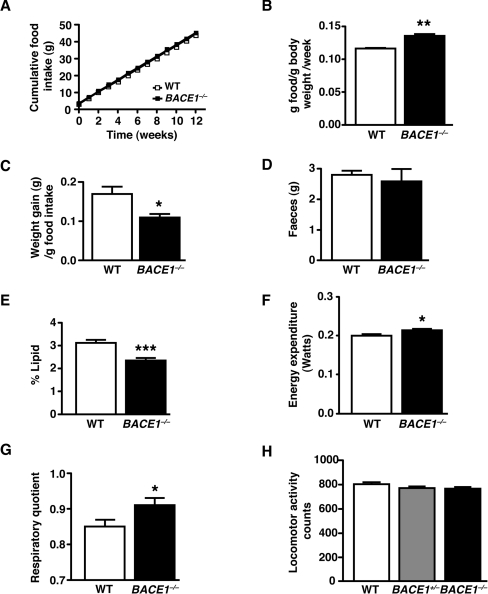
Figure 2. BACE1−/− mice have increased relative food intake and energy expenditure.
(A) Cumulative food intake, measured over 12 weeks, in 3-month-old male mice of the indicated genotypes. (B) Food intake per mouse per week normalized by body mass (relative food intake). (C) BACE1−/− mice have decreased feed efficiency compared with the WT controls. Results in (A–C) are from 5–7 animals of each genotype. (D) Mean mass of faeces over 24 h for WT and BACE1−/− mice. (E) Lipid content of faeces in WT and BACE1−/− mice. Results in (D) and (E) are from seven animals of each genotype. (F) Energy expenditure determined by indirect calorimetry in 8-month-old WT and BACE1−/− mice. (G), BACE1−/− mice have an increased RQ compared with the WT mice. Results in (F) and (G), WT, n=14 and BACE1−/−, n=12. (H) Effect of genotype on locomotor activity. WT, n=9; BACE1+/−, n=10; BACE1−/−, n=6. Results are means±S.E.M. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001.