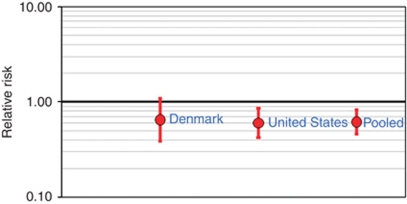
Figure 1.
Forest plot for meta-analysis of US and Danish studies of the association between long-term vs never/rare aspirin use and risk of Hodgkin lymphoma. The circles show the estimated odds ratios and the vertical lines show the 95% confidence intervals. The summary (pooled) odds ratio was 0.62 (95% confidence interval: 0.46, 0.82) based on both random-effects and fixed-effects models, with no evidence of heterogeneity between studies (P=0.80). Study populations included in the meta-analysis were from the United States (565 cases, 679 controls (Chang et al, 2004)) and Denmark (1659 cases, 8089 controls; present study). The meta-analysis and forest plot were performed using Episheet (Rothman, 2008).