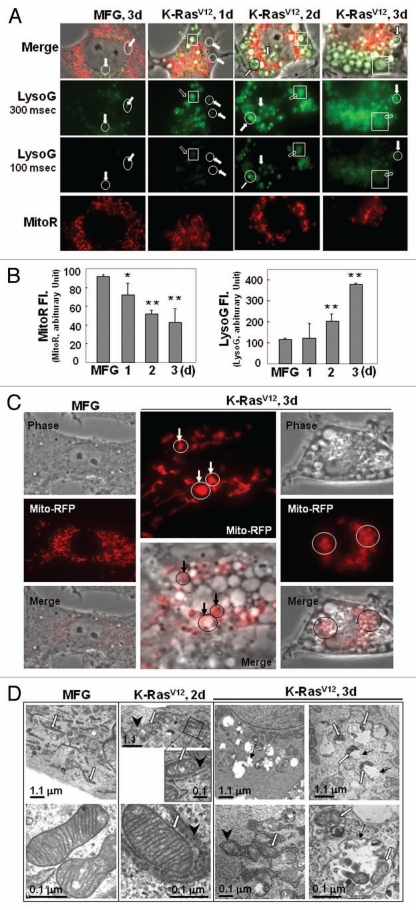
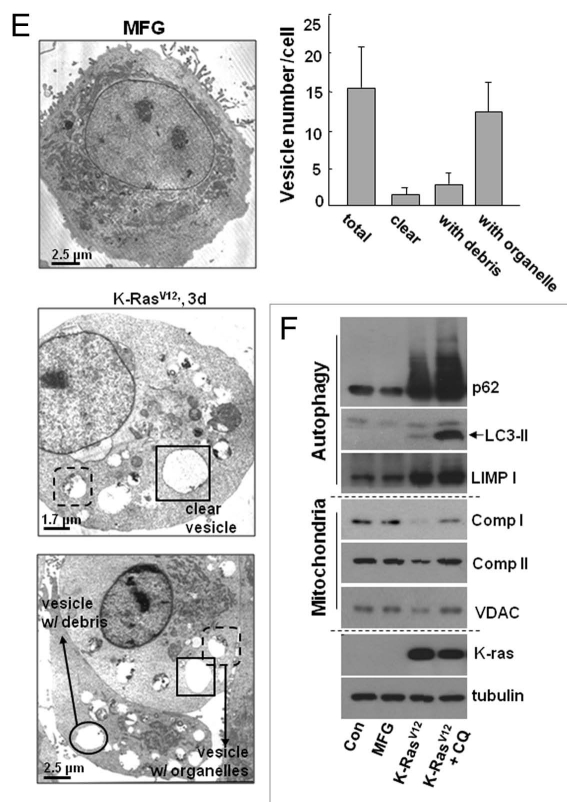
Figure 2.
K-RasV12 activates autophagic vesicle formation, accompanied by mitochondrial loss. Rat2 cells were infected with retrovirus harboring K-RasV12 for the indicated periods. (A) Mitochondrial mass decrease and lysosomal mass increase were visualized after co-staining the cells with 50 nM LysoTracker Green (LysoG) and 200 nM MitoTracker Red (MitoR) without fixation using a Plan-Apochromat x100, 1.4 NA oil-immersion objective. Green indicates lysosomes and red indicates mitochondria. (B) Flow cytometric analysis was performed for quantification of mitochondrial mass (left part) or lysosomal mass (right part) of the co-stained cells with MitoR and LysoG. (C) To visualize live images, Rat2 cells were transiently transfected with mtRFP and infected with K-RasV12 retrovirus, and further cultured for 3 d on chamlide™ chamber as described in ‘Materials and Methods’. Targeting of mtRFP-labeled mitochondria into autophagic vesicles was visualized without fixation using a Plan-Apochromat x100, 1.4 NA oil-immersion objective. Representative images are presented. (D) Representative electron microscopic images are presented. The open arrows indicate representative mitochondria within autophagosome, thin arrows indicate autophagosome and arrowheads indicate endoplasmic reticulum entrapping mitochondria. (E) Numbers of total vesicles, clear empty vesicles (square), vesicles with debris (circle) and vesicles with organellar remnants (dotted square) were counted from 26 whole cell electron microscopic images (3,000x or 4,400x) of K-Ras infected Rat2 cells (right part). Representative images are shown in the left part. (F) Western blot analysis. After infected by K-RasV12 retrovirus for 24 h, cells were replenished with RPMi media containing 10 µM chloroquine (C6628, Sigma-Aldrich) for 2 d. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 vs. MFG control.