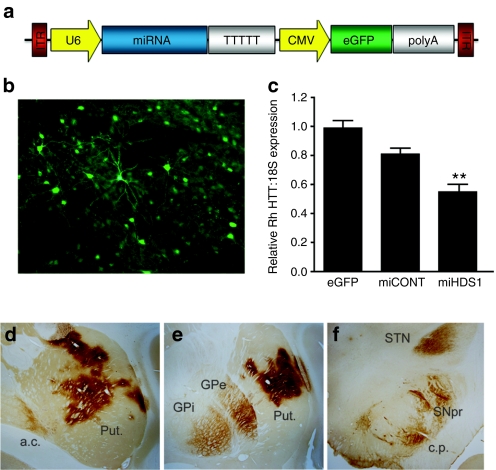
Figure 1.
HTT suppression and AAV distribution following injection into the putamen. (a) Cartoon of the AAV2/1 vector depicting miRNA expression driven from the Pol III promoter, U6, and eGFP driven from the Pol II promoter, CMV. (b) Unstained, eGFP fluorescence was used to define AAV2/1 transduced regions of the putamen. (c) Relative rhesus HTT/18S expression was determined by QPCR. AAV-miHDS1-injected putamen showed a significant 45% reduction in HTT expression compared to AAV-eGFP-injected controls (mean ± SEM, P < 0.01). Anti-eGFP immunohistochemistry was used to identify (d) transduced regions of the putamen and (e) other basal ganglia nuclei such as the internal and external segments of the globus pallidus, (f) the substantia nigra pars reticulata and the subthalamic nucleus. a.c., anterior commissure; c.p., cerebral peduncle; GPe, exterior segment of the globus pallidus; GPi, interior segment of the globus pallidus; Put., putamen; QPCR, quantitative polymerase chain reaction; SNpr, substantia nigra pars reticulata; STN, subthlamic nucleus.