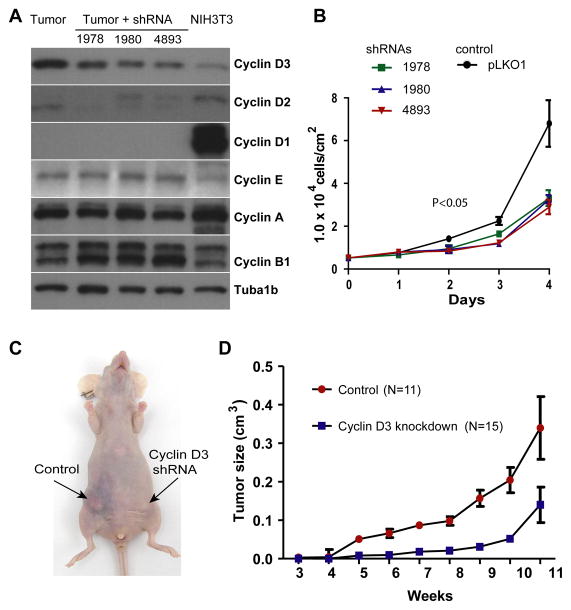
Fig. 7. Ablation of Cyclin D1 and Cyclin D3 impairs the proliferation of ErbB2-induced cancer cells.
A. Western blot analysis of D-type cyclins, Cyclin E, Cyclin A, and Cyclin B in primary ErbB2-induced mammary cancer cells that lack expression of endogenous Cyclin D1. Tubulin (Tuba1b) was used as a loading control. Mammary tumor cells were infected with lentiviral vectors that express three different shRNAs to knock down the expression of Cyclin D3. B. viable cell count over a 4-d period to determine growth rates of three Cyclin D1/D3-deficient cancer cell lines compared to control cells that lack only Cyclin D1 (pLKO1); P, U-test. C. Recipient female that developed mammary tumors after orthotopic transplantation of Cyclin D1-single (control) or Cyclin D1/D3-double deficient cells. D. Growth curve of Cyclin D1-deficient mammary tumors in the presence (control) or absence of Cyclin D3.