Fig. 1.
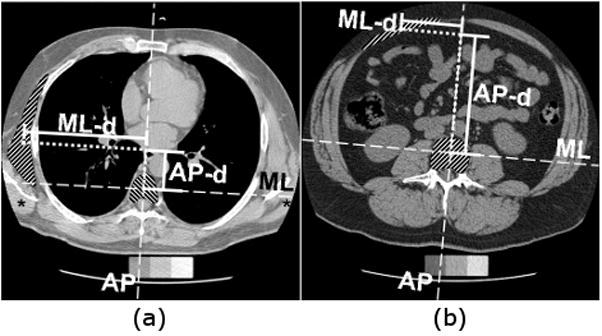
Measurement of muscle position in transverse plane scans. Position was calculated as the difference between centroid locations of muscle and vertebral body in the ML direction (ML-d) and in the AP direction (AP-d), shown here for (a) the left serratus anterior muscle at the T7 vertebral level, and (b) the left rectus abdominis muscle at the L3 vertebral level. Asterisks (*) denote examples of a muscle (latissimus dorsi) that extends outside the QCT image field of view, and thus was not measured.
