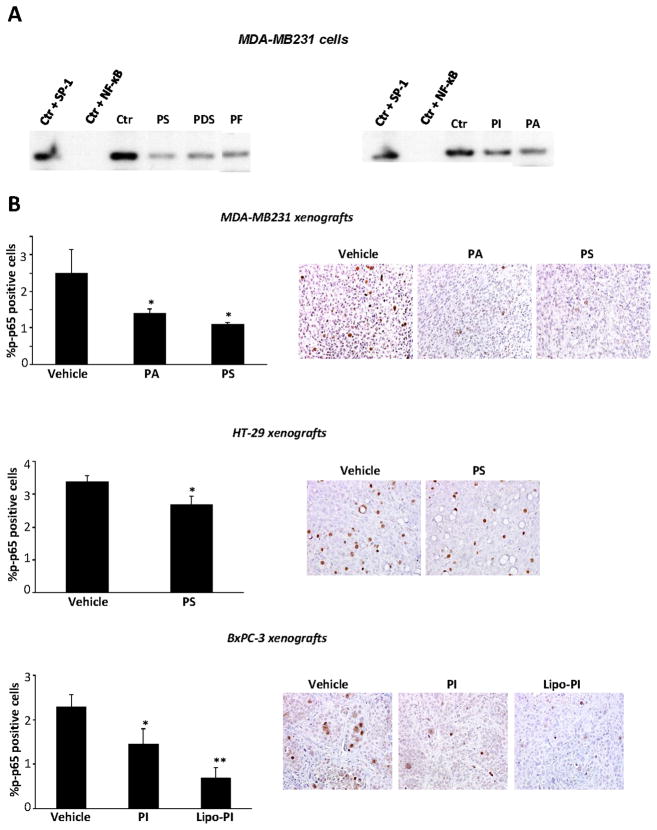
Fig. 5. Phospho-NSAIDs inhibit NF-κB activation in breast, colon and pancreatic cancer cells and in xenografts.
A: Phospho-NSAIDs inhibit constitutive NF-κB activation. EMSA for NF-κB of nuclear fractions isolated from MDA-MB-231 cells after 4 h-treatment without or with each phospho-NSAID at 1.5xIC50. To determine the specificity of the NF-κB transcription factor-DNA complex, the control nuclear fraction was incubated in the presence of 100-fold molar excess of unlabeled oligonucleotide containing the consensus sequence for either the specific (+ NF-κB) or an unspecific (+ SP-1) transcription factor. A representative image is shown. B: NF-κB (p-p65) levels from MDA-MB-231, HT-29 or BxPC-3 tumors were determined by immunohistochemistry using an anti-p-p65 antibody. The percentage of p-p65-positive cells is randomly selected fields was determined and averaged for each xenograft. Values are mean ± SEM; *, p<0.05, **, p<0.002, compared to control. Representative images are shown; magnification 200X.