Fig. 4.
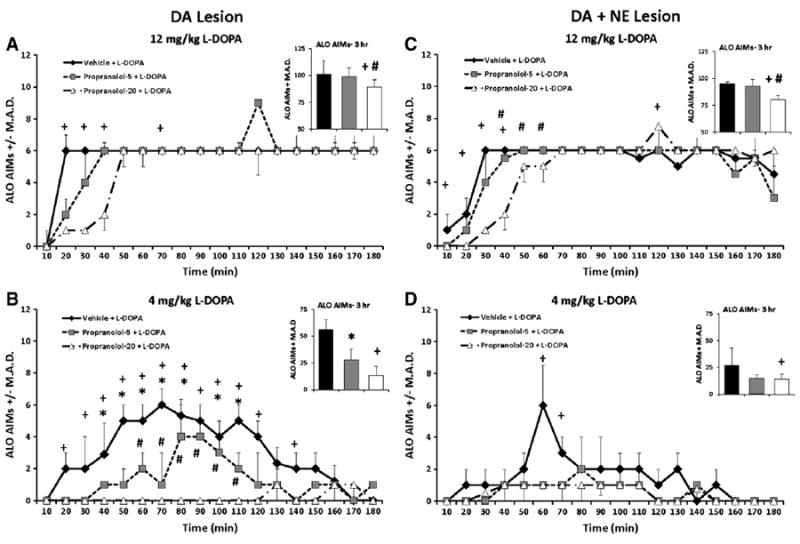
ALO AIMs in rats pretreated with 0, 5, and 20 mg/kg propranolol (PRO) in L-DOPA-primed DA (n = 10) and DA + NE (n = 9) lesioned rats prior to 4 and 12 mg/kg L-DOPA. Nonparametric Friedman ANOVAs were used to analyze potential treatment differences in ALO AIMs at each time point (10–180 min). In the DA lesion group, pretreatment with 20 mg/kg PRO reduced ALO AIMs at 20–40 and 70 min following 12 mg/kg L-DOPA (A). Following 4 mg/kg L-DOPA, 20 mg/kg of PRO attenuated ALO AIMs from 20 to 120 min and 140 to 150 min, while 10 mg/kg conveyed anti-dyskinetic effected from 40 to 110 min and at 150. PRO 5 and 20 mg/kg differed from 60 to 110 min (B). In the DA + NE lesion group, 20 mg/kg PRO dose-dependently reduced ALO AIMs 10–40 and at 120 min following 12 mg/kg L-DOPA (C), while reduced ALO AIMs were observed following 20 mg/kg PRO and 4 mg/kg L-DOPA only at 60 and 70 min time points (D). *P<0.05 for Vehicle vs. PRO-5, +P<0.05 for Vehicle vs. PRO-20 and #P<0.05 for PRO-5 vs. PRO-20. All significant differences were between groups at the same time point (line graphs) or total time (insets). Data presented as median ALO AIMs ± M.A.D.
