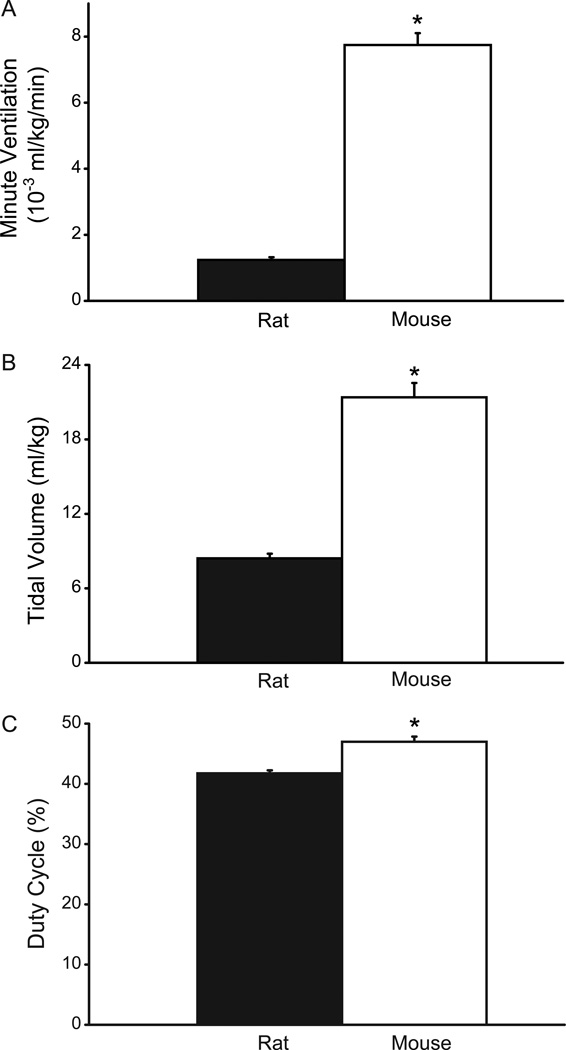
Fig. 1.
Ventilatory parameters in adult rats (n=10) and mice (n=9) measured in awake, unrestrained animals using whole body plethysmography. A. Minute ventilation (×10−3 ml/kg/min); B. tidal volume (ml/kg); and, C. duty cycle (percent inspiratory time out of total cycle time). All ventilatory parameters were significantly greater in the adult mouse compared to the rat even when adjusted for differences in body weight. Data are mean (± SE). *, denotes statistically significant difference compared to the rat (p<0.05).