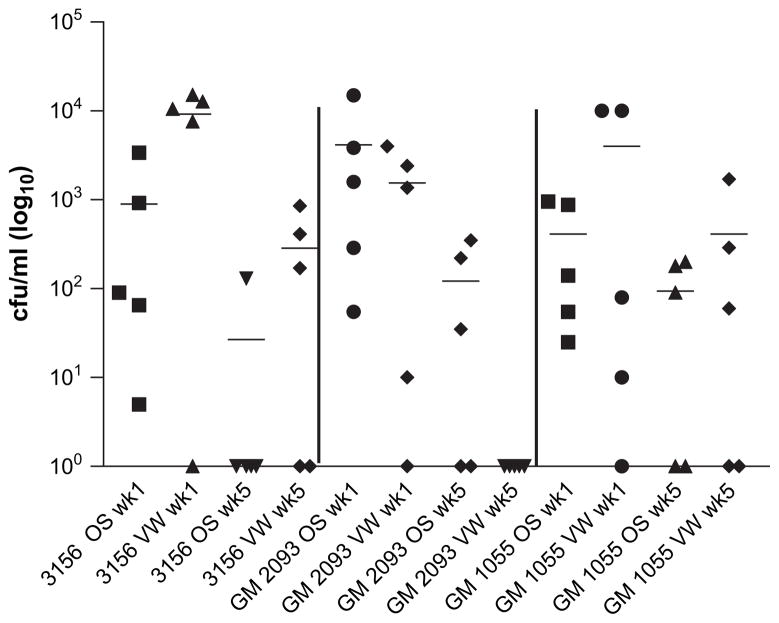
Fig. 3.
Fresh isolation of a C. albicans strain from an in vivo site is not a fundamental criterion in order to establish colonization. BALB/c mice (n = 5) were induced into a state of pseudoestrus and inoculated orally and vaginally as described with two clinical C. albicans isolates, GM2093 and GM1055, and the laboratory strain NCPF3156. Oral swabs and vaginal washings were collected at weekly intervals and C. albicans CFU/ml in individual mice are shown at 1 and 5 weeks after inoculation. All three strains colonized both sites at week 1, but at week 5 one or both mucosal sites only in up to 60% of mice and less persistently than 529L (compare with Fig. 1).