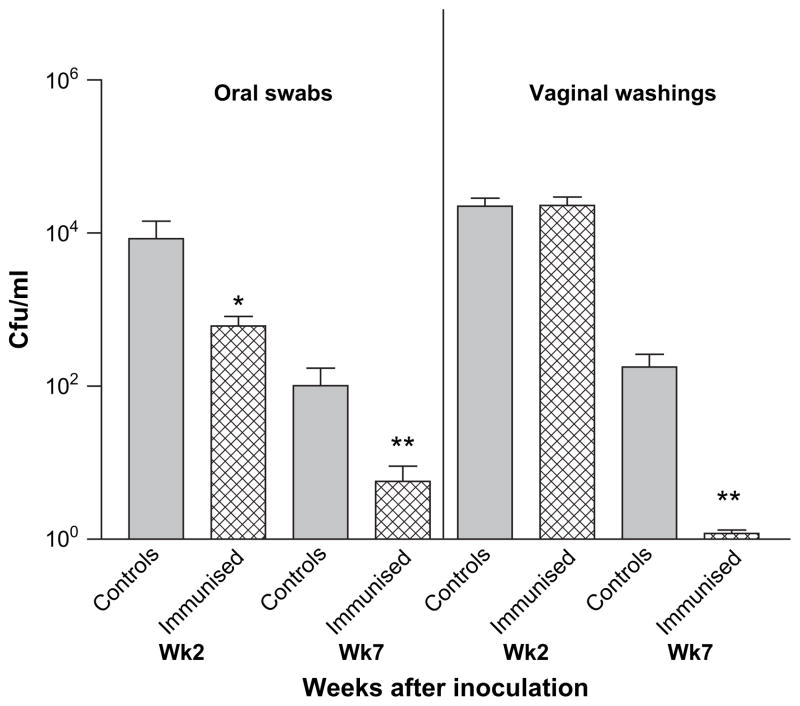
Fig. 6.
Fungal burdens are significantly reduced after mucosal immunization with a putative C. albicans virulence factor. Balb/c mice (n = 10) induced into a state of pseudoestrus (see Section 2) were immunized intranasally with 5 μg of C. albicans secreted aspartyl protease (Sap2) and 1 μg cholera toxin or PBS (control). Two weeks after immunization, mice were challenged orally and vaginally with C. albicans 529L as described. Weekly oral swabs and vaginal washings were collected and fungal burdens followed for an additional 5 weeks (mean ± S.E.M.). Significant reduction in fungal burdens was observed orally at week 2 (*P < 0.05) and at week 7 both orally (**P < 0.001) and vaginally (**P < 0.0001). The data are representative of two independent experiments.