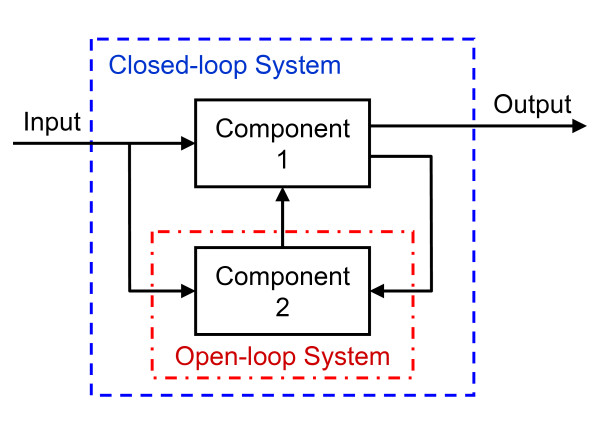
Figure 6.
A schematic diagram of a two-component closed-loop system. The behavior of a closed-loop system, enclosed within the blue dotted box, is characterized by measurements of variables that provide input to and that reflect the output of the overall system. These variables are depicted as lines that cross the system boundary, depicted by the dotted blue box. The internal variables that are not observed facilitate communication among the system components. Output variables for one component may provide input variables for another component. This internal communication may alter system behavior such that the same system input may result in different system output depending on the internal state of the system. Measurement of internal variables enables characterizing the causal relationships between input variables and output variables for a specific component within an intact system. Ideally, measuring these internal variables reduces complex closed-loop system to a series of connected open-loop systems, as depicted by the red dot-dashed boxes. In an open-loop system, changes in input variables result in a defined response of the system.