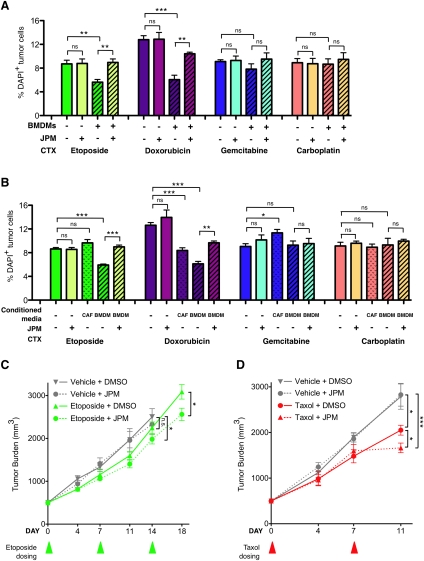
Figure 6.
Cathepsin-mediated chemoprotection is relevant to other chemotherapies and additional in vivo models. (A) Percentage of DAPI+ (dead) tumor cells in mono- or coculture of the TS1 cell line with BMDMs 48 h after etoposide (20 μM), doxorubicin (300 nM), gemcitabine (400 nM), carboplatin (50 μM), or DMSO treatment. Coculture with BMDMs was protective against treatment with etoposide and doxorubicin, but not gemcitabine or carboplatin. As with Taxol, the protective effect observed in BMDM coculture was significantly abrogated by the cathepsin inhibitor JPM (10 μM). (B) Cell death in tumor cells cultured alone or in the presence of wild-type (WT) BMDM-CM or CAF-CM 48 h after treatment with etoposide, doxorubicin, gemcitabine, carboplatin, or DMSO control. For all graphs in A and B, data are from three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate. (*) P < 0.05; (**) P < 0.01; (***) P < 0.001; (ns) not significant. (C) FVB/n mice orthotopically implanted with TS1 cells were treated with etoposide (10 mg/kg per week). Addition of JPM (100 mg/kg per day) significantly improved response to etoposide. (*) P < 0.05. The etoposide/JPM combination treatment also significantly reduced tumor growth compared with the vehicle-treated group on day 14 (endpoint for the vehicle- and JPM-treated mice due to tumor burden limits). n = 8–10 mice per group. (D) Athy/Nu mice orthotopically implanted with MDA-231 cells were treated with MTD Taxol (25mg/kg per week) or vehicle control. Addition of JPM (100 mg/kg per day) significantly improved response to Taxol in this preclinical xenograft model. (*) P < 0.05 compared with Taxol alone; (***) P < 0.001 compared with vehicle; n = 9–12 mice per group. Triangles below the graphs in C and D indicate the time points at which etoposide and Taxol, respectively, were administered.